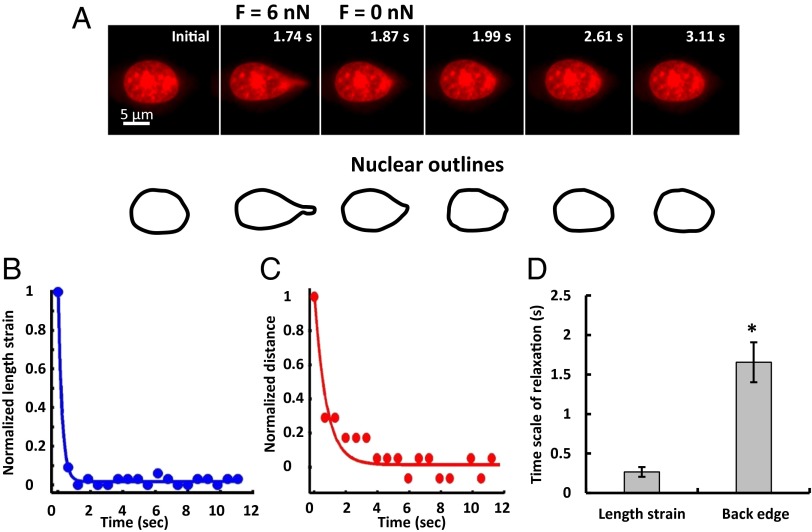
Fig. 2.
Rapid nuclear relaxation upon force release. (A) A typical nucleus is shown at the indicated times. After the nucleus deformed when the micropipette tip sealed to the nuclear surface with a suction force of 6 nN was translated, it rapidly relaxed back to its original shape and position on detachment from the micropipette tip; steady state after detachment was achieved in a few seconds. (B and C) The time-dependent recovery of the length strain (which is a measure of nuclear deformation, blue circles) and back edge distance (red circles) could be described by single exponential fits (solid lines), with the length strain relaxation being much faster than the back edge relaxation; quantification is shown (D). *P < 0.05, n = 10.