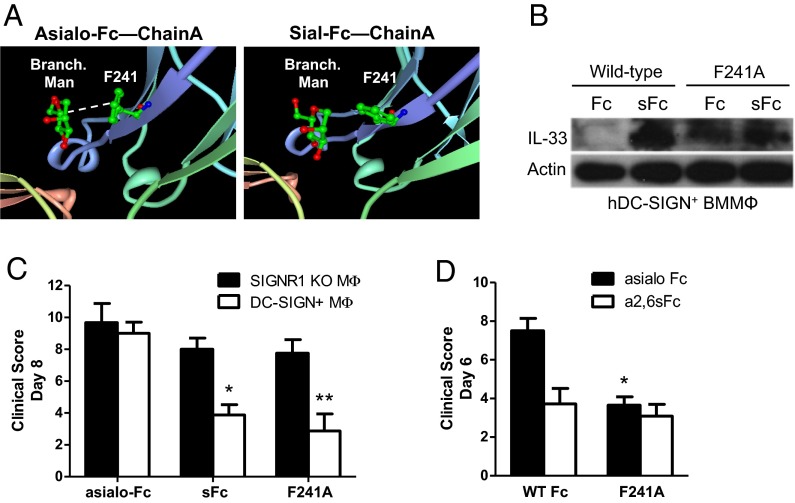
Fig. 1.
F241A is capable of suppressing serum-induced arthritis. (A) Schematic depiction of the interaction between mannose residues of the nonsialylated core glycan (Asialo-Fc) with the phenylalanine residue at position 241 of the Cγ2 domain. Upon sialylation (Sial-Fc) this interaction no longer occurs, resulting in a higher conformational flexibility of the Fc portion to switch between the so-called open and closed conformations. (B) hDC-SIGN+ bone marrow-derived macrophages were pulsed with sialylated (sFc) or nonsialylated (Fc) wild-type Fc or F241A Fc. Whole-cell extracts were used to analyze IL-33 production by Western blotting. Actin served as loading control. (C) BMMΦs from either SIGN-R1−/− or hDC-SIGN+ mice were pulsed with nonsialylated wild-type Fc (asialo-Fc), sialylated wild-type Fc (sFc), or F241A. After extensive washes, the cells were adoptively transferred into C57BL/6 mice and then challenged with K/BxN serum. (D) hDC-SIGN+ BMMΦs were pulsed with either asialylated (asialo Fc) or sialylated (α2,6sFc) variants of wild-type Fc or F241A. The cells were adoptively transferred into C57BL/6 mice and then challenged with K/BxN serum. Means ± SEM are plotted; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 determined by Tukey’s post hoc test.