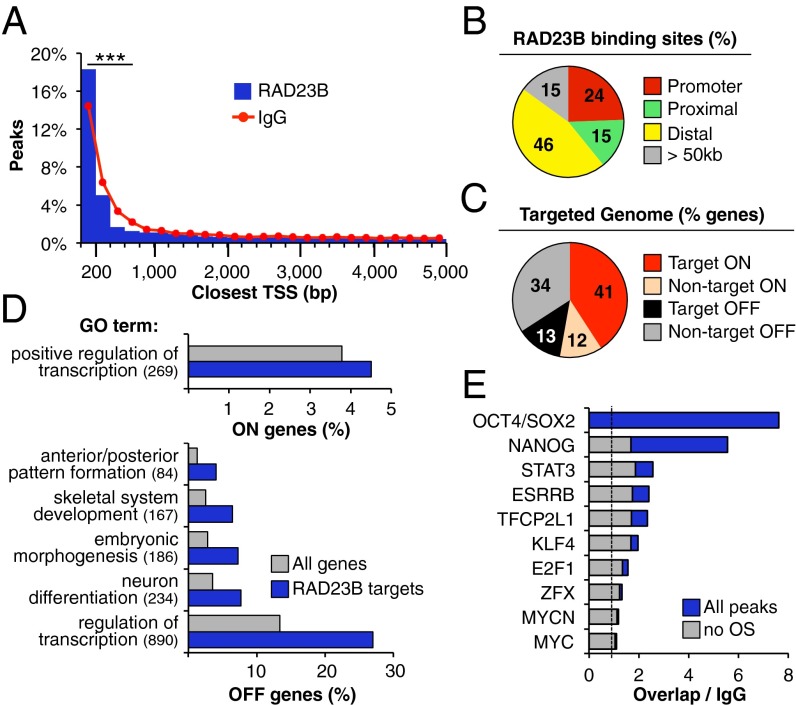
Fig. 1.
Genome-wide distribution of RAD23B binding. (A) Distribution of RAD23B and control (IgG) ChIP-seq peaks around RefSeq gene TSS in D3 mESCs (annotated list of RAD23B binding sites in Dataset S1). Distance to the closest TSS is binned in 200-bp intervals. The two samples show a significantly different distribution up to 800 bp away from the TSS (***P < 10−14, two-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction). (B) Percent distribution of RAD23B binding between promoters (0–500 bp from TSS), proximal (500–5,000 bp from TSS) and distal (5–50 kb from TSS) gene regions. Fifteen percent of binding events are more than 50 kb away from any annotated TSS (gray bar). (C) Percent of active (ON, red shades) and inactive (OFF, gray shades) genes in D3 mESCs (8) with a RAD23B binding site within 5 kb from their TSS. (D) GO of active (ON, Upper) and inactive (OFF, Lower) genes with a RAD23B binding site within 5 kb from their TSS compared with all ON/OFF genes in D3 mESCs. In parentheses is the number of target genes in each GO term. Bonferroni P value < 10−5 for all categories (complete table in Dataset S1; Polycomb binding in Fig. S2B). (E) Overlap between RAD23B binding sites and ChIP-seq peaks of major transcription factors in mESCs (24, 70). Plotted is the percentage of RAD23B peaks overlapping with a given TF relative to the overlap in control (IgG) ChIP-seq peaks (dashed line: ratio to IgG = 1, background levels). In blue is the overlap when considering all TF binding sites, in gray is the overlap when considering only those TF binding sites that do not overlap with OCT4/SOX2 peaks. Additional overlap analyses in Fig. S2. Data in A–E are from one of two highly overlapping RAD23B ChIP-seq experiments in D3 mESCs (Fig. S1).