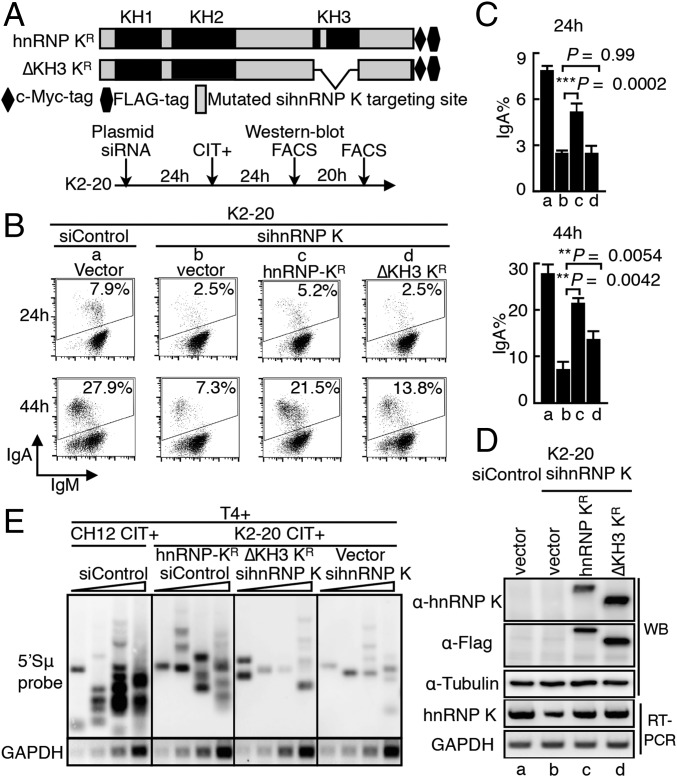
Fig. 4.
Requirement for the RNA-binding domains of hnRNP K for CSR. (A) Representation of the siRNA-resistant and epitope (c-Myc-FLAG)-tagged hnRNP K constructs. WT and KH3-deleted hnRNP K are designated as hnRNP KR and ΔKH3 KR, respectively. (B) CSR complementation assay performed by cotransfecting K2-20 cells with KR constructs and hnRNP K siRNA. The percentages of IgA-switched cells are indicated in the FACS profiles. (C) Efficiency of CSR rescue calculated from three independent experiments. (D, Upper) Western blot (WB) analysis shows the protein expression of the indicated KR constructs in K2-20 cells. (Lower) RT-PCR analysis of hnRNP K mRNA expression using primers M4 and M5 (Fig. S2C). (E) Southern blot analysis of LM-PCR–based DNA break assay using T4 polymerase-treated (T4+) DNA samples as in Fig. 3. K-20 cells were cotransfected with the indicated siRNAs and the hnRNP K-expressing constructs resistant to sihnRNP K-mediated degradation. After 24 h of transfection, cells were stimulated with CIT and were harvested for DNA break assay 24 h later.