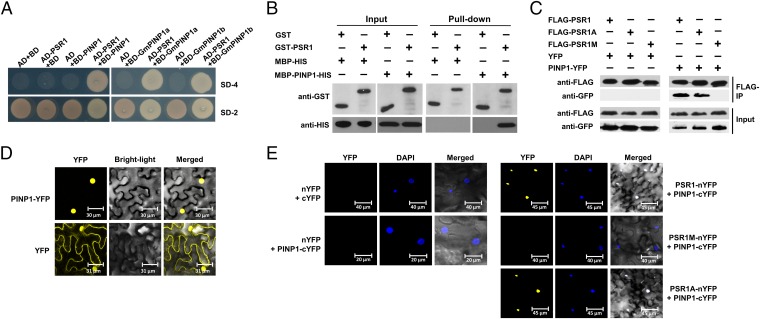
Fig. 1.
PSR1 interacts with a plant nuclear protein PINP1. (A) PSR1 interacts with PINP1 in yeast. Yeast strain AH109 was transformed with the bait plasmid pGBKT7 (BD) carrying PSR1 together with the prey plasmid pGADT7 (AD) carrying PINP1, GmPINP1a, or GmPINP1b. Transformants were selected on minimal medium lacking adenine, tryptophan, histidine, and leucine (SD-4). (B) PSR1 and PINP1 interact in vitro. GST–PSR1 and MBP–PINP1–HIS were expressed in E. coli. Coprecipitation of PINP1 with PSR1 was examined by Western blotting before (input) and after affinity purification (pull-down) using glutathione agarose beads. (C) PSR1 and PINP1 interact in planta. Total proteins were extracted from N. benthamiana leaves expressing PINP1–YFP and FLAG–PSR1. The immune complexes were pulled down by using anti-FLAG agarose gel, and the coprecipitation of PINP1 was detected by Western blotting. (D) PINP1 is exclusively located in the nucleus. PINP1–YFP was expressed in N. benthamiana through Agro-infiltration. Fluorescence was detected from epidermal cells in the infiltrated tissues by confocal microscopy at 48 h postinoculation (hpi). (E) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation analysis showing PSR1/PINP1 interaction in the nuclei of plant cells. PSR1–nYFP and PINP1–cYFP were coexpressed in N. benthamiana through Agro-infiltration. Fluorescence was detected by confocal microscopy at 48 hpi. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. These experiments were repeated three times with similar results.