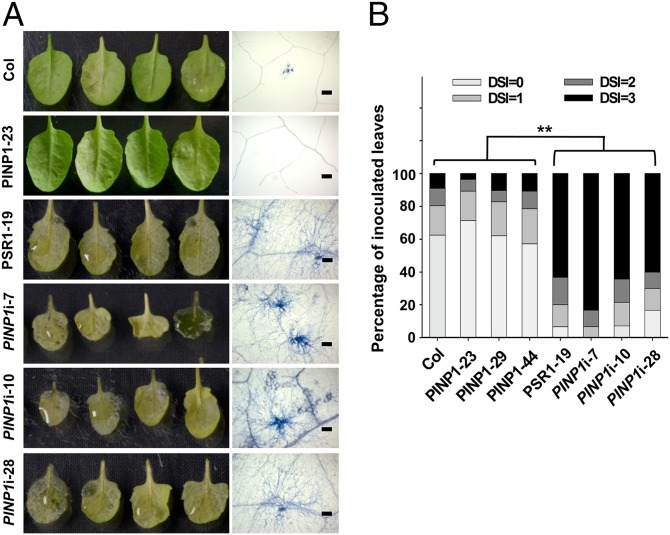
Fig. 3.
Silencing of PINP1 leads to hypersusceptibility of Arabidopsis to P. capsici strain LT263. Adult leaves of 4-wk-old wild-type plants (Col-0), 4-wk-old PINP1-overexpressing plants (PINP1-23), 5.5-wk-old PSR1-expressing plants (PSR1-19), and 7-wk-old PINP1-silenced plants were detached and inoculated with zoospore suspension of P. capsici strain LT263 (1 × 105 zoospores per mL). Disease symptoms were monitored at 3 d postinoculation (dpi), and the disease severity index (DSI) of each leaf was determined. Forty leaves from 15–20 plants were inoculated and analyzed in each line. Note that 4-wk-old PSR1-expressing or PINP1-silenced plants were too small for inoculation. (A) Photos of inoculated leaves (Left) and microscope pictures of Phytophthora hyphae extension (Right) in the leaves at 3 dpi. Trypan blue was used to stain the hyphae for visualization. (Scale bars: 250 μm.) (B) Quantitative analysis of disease severity. **P < 0.01 (as determined by the Wilcoxon rank-sum test). This experiment was repeated three times with similar results.