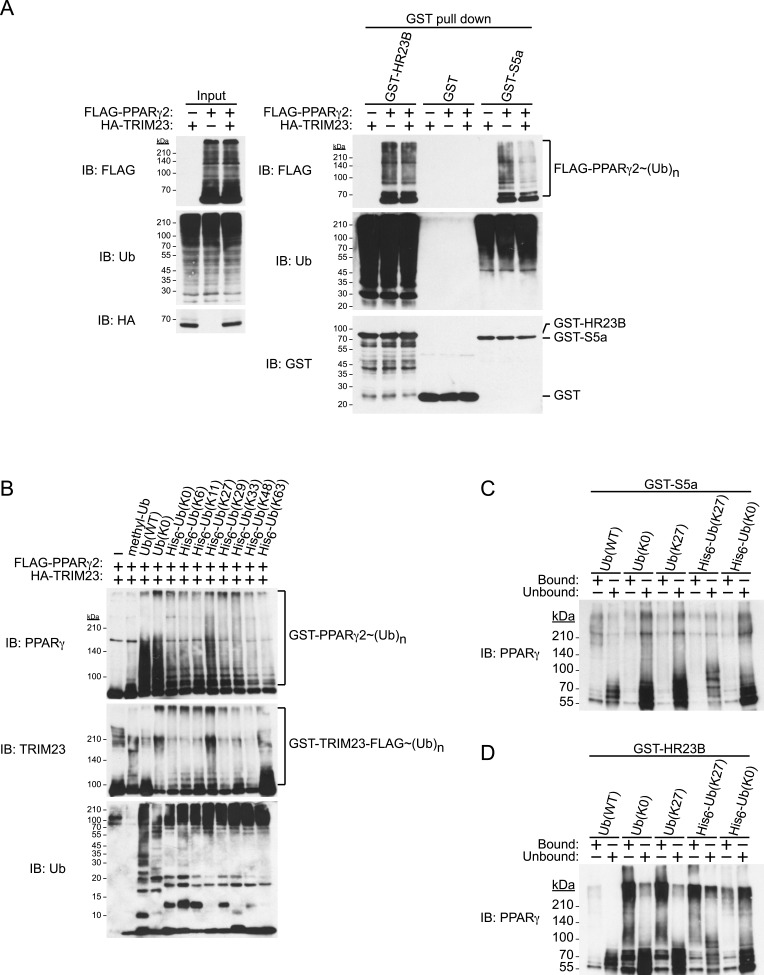
Figure 9. TRIM23 mediates atypical polyubiquitin conjugation of PPARγ2, leading to reduced recognition of ubiquitinated PPARγ2 by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a.
(A) PPARγ2 polyubiquitination by TRIM23 leads to reduced recognition by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a. HEK293T cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding FLAG-PPARγ2 and/or HA-TRIM23 were lysed. GST, GST-HR23B, and GST-S5a were resuspended with cell lysates, followed by pull-down with glutathione Sepharose beads. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (B) In vitro PPARγ2 polyubiquitination by TRIM23. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated combinations of ATP, various ubiquitin mutants, His6-E1, E2 (UbcH5C), His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG, and GST-PPARγ2. Reaction mixtures were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-PPARγ (top), anti-TRIM23 (middle) or anti-Ub (bottom) antibodies. The positions of GST-PPARγ2 or His6-GST-TRIM23-FLAG modified by various numbers of ubiquitin moieties are indicated. (C and D) Conjugation of PPARγ2 with M1- and/or K27-linked polyubiquitin chains leads to reduced recognition by the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a. An in vitro ubiquitination assay was performed with the indicated combinations of ATP, ubiquitin mutants, His6-E1, E2 (UbcH5C), TRIM23-FLAG, and PPARγ2. Reaction mixtures were subjected to GST pull-down assay. PPARγ2-ubiquitin conjugates were incubated with GST-S5a (C) or GST-HR23B (D) prebound to glutathione Sepharose beads. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting using a PPARγ antibody. Equivalent amounts of bound and unbound fractions were loaded in each lane.