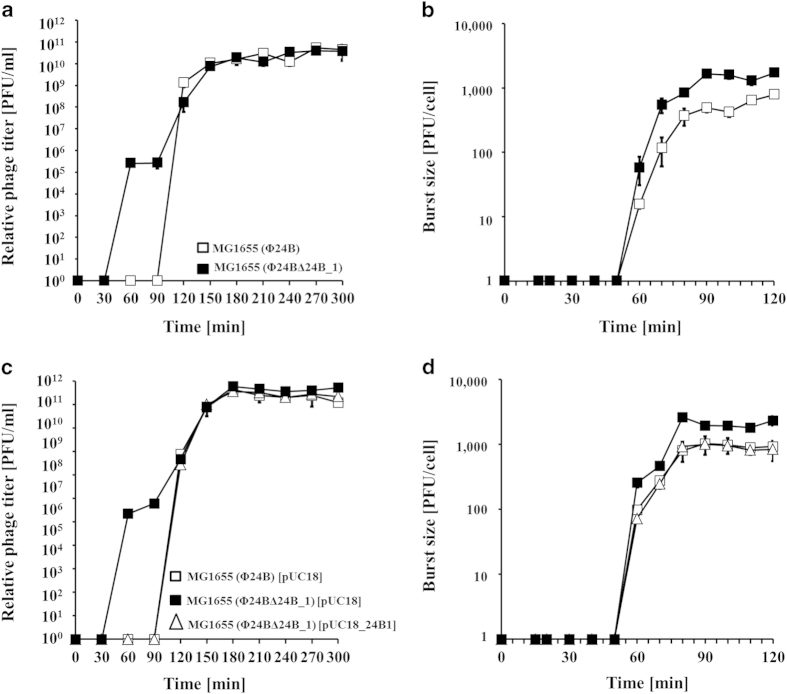
Figure 4. Development of Φ24B and Φ24B∆24B_1 bacteriophages after prophage induction or phage infection at 37 oC.
E. coli MG1655 bacteria bearing no plasmid (□, ■ in panels a and b), plasmid pUC18 (□, ■ in panels c and d) or plasmid pUC18_24B1 (∆ in panels c and d) were hosts for phage development. The hosts were either lysogenic for Φ24B (□ in panels a and c) or Φ24B∆24B_1 (■, ∆ in panels a and c), or infected with Φ24B (□ in panels b and d) or Φ24B∆24B_1 (■, ∆ in panels b and d). Phage lytic development was initiated by addition of mitomycin C to final concentration of 1 μg/ml (panels a and c) or phage infection (panels b and d) at time 0. The presented results are mean values from three independent experiments with error bars indicating SD (note that in the most cases, the bars are smaller than sizes of symbols). Results are shown as PFU (plaque forming units) per one ml of bacterial culture (a, c) or per cell (b, d).