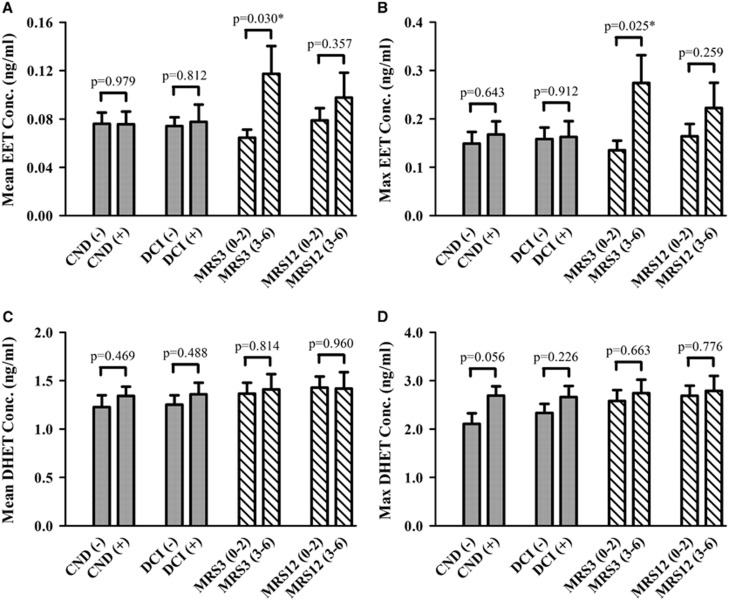
Figure 2.
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) eicosanoid levels in outcome groups. Mean epoxyeicosatrienoic acid (EET) (A), maximum EET (B), mean dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (DHET) (C), and maximum DHET (D) levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) are compared in outcomes groups. Acute outcomes (solid bars) included the presence or absence of delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) and clinical neurologic deterioration (CND) up to 14 days after the hemorrhage. Long-term outcomes (stripped bars) were determined by global functional recovery at 3 and 12 months using the Modified Rankin Scale (MRS) and were dichotomized into favorable (MRS 0 to 2) and unfavorable (MRS 3 to 6) groups. The mean and maximum EET and DHET CSF levels for each patient were calculated and were used to compare the mean±s.e.m. of the CYP eicosanoid levels in outcome groups using t-test with Welch's correction as appropriate. Statistical significance established at *P<0.05.