Figure 1.
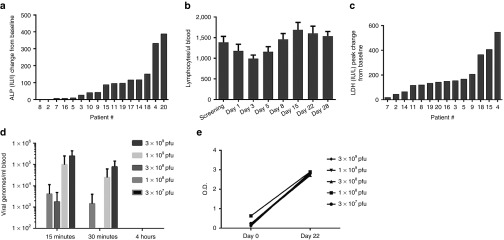
Toxicity of vvDD administration and acute pharmacokinetics. Blood samples were collected at various time points before and after virus administration. The enzyme activities in the serum and lymphocyte numbers in peripheral blood mononuclear cells were quantified. (a) Peak alkaline phosphatase levels (IU/l) relative to the baseline values before virus administration. (b) Median absolute lymphocyte count over time. (c) Lactate dehydrogenase peak levels (IU/l) relative to the baseline. (d) Recovery of serum vvDD DNA by qPCR at 15 minutes, 30 minutes, and 4 hours postinjection. The level of detection was 666 copies/ml and the level of quantification was 3333 copies/ml. At the 30-minute time point, viral DNA was detectable in patients treated at dose levels of 1.00E+08 and 3.00E+08 but below the level of quantification (at least 666 copies/ml but less than 3,333 copies/ml). This was also true at the 4-hour time point for patients treated at the two highest dose levels (1.00E+09 and 3.00E+09). The values displayed graphically represent serum vvDD DNA in copies/ml only in cases in which the detected level was greater than 3,333 copies/ml (the level of quantification). (e) Antibody response to viral administration demonstrating baseline and day 22 post-vvDD administration levels of anti-VV antibodies as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 12 of 17 patients. A 1.0 OD value represents a >50-fold induction of antibody.
