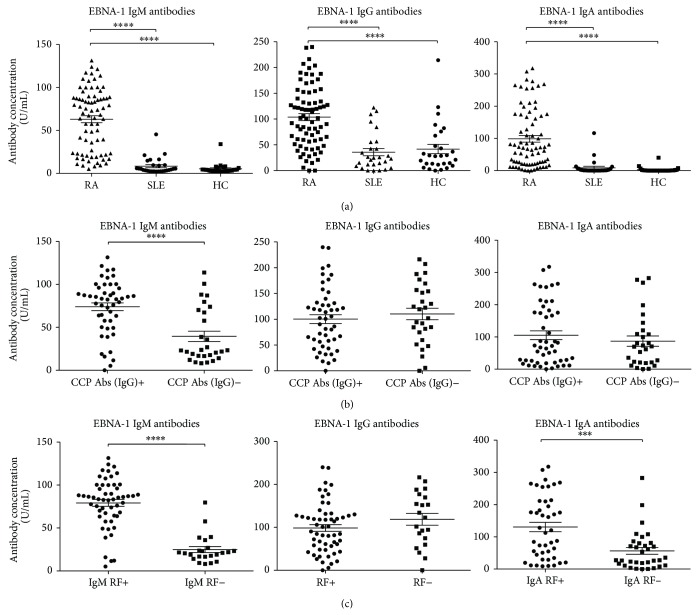
Figure 2.
Scattergrams showing individual levels of EBNA-1 IgG/IgM/IgA in plasma from RA patients, SLE patients, and HCs and individual levels of EBNA-1 IgG/IgM/IgA from RA patients divided into CCP IgG positives and negatives and divided into IgA RF and IgM RF positives and negatives. (a) EBNA-1 IgM/IgG/IgA levels. RA patients (n = 77), SLE patients (n = 28), and HCs (n = 28). (b) EBNA-1 IgM/IgG/IgA levels sorted into CCP IgG positives (n = 49) and CCP IgG negatives (n = 28). RA patients total (n = 77). (c) EBNA-1 IgA levels sorted in IgA RF states, IgA RF positives (n = 44) and IgA RF negatives (n = 33). EBNA-1 IgG levels sorted in RF states, IgM or IgA RF positives (n = 56) and RF negatives (n = 21). EBNA-1 IgM levels sorted in IgM RF states, IgM RF positives (n = 54) and IgM RF negatives (n = 23). RA patients total (n = 77). Groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Concentrations of antibodies are presented in arbitrary units. Statistical significant differences are indicated with ∗, ∗∗, ∗∗∗, or ∗∗∗∗ for P values less than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, or 0.0001, respectively.