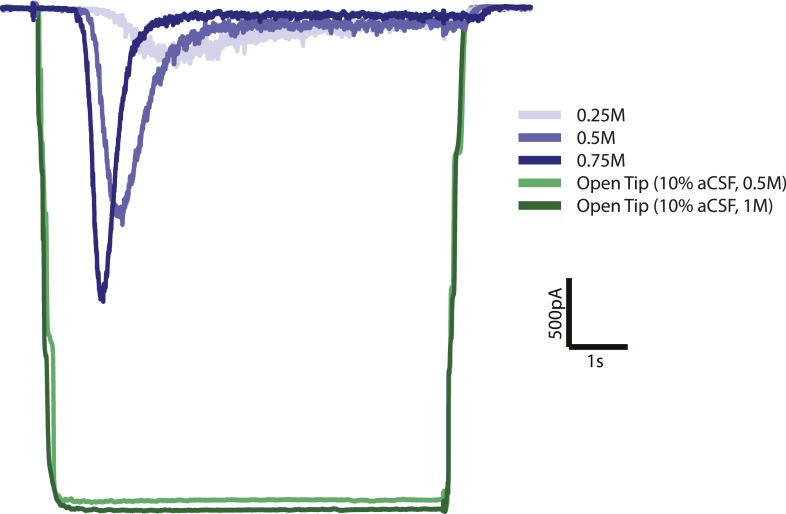
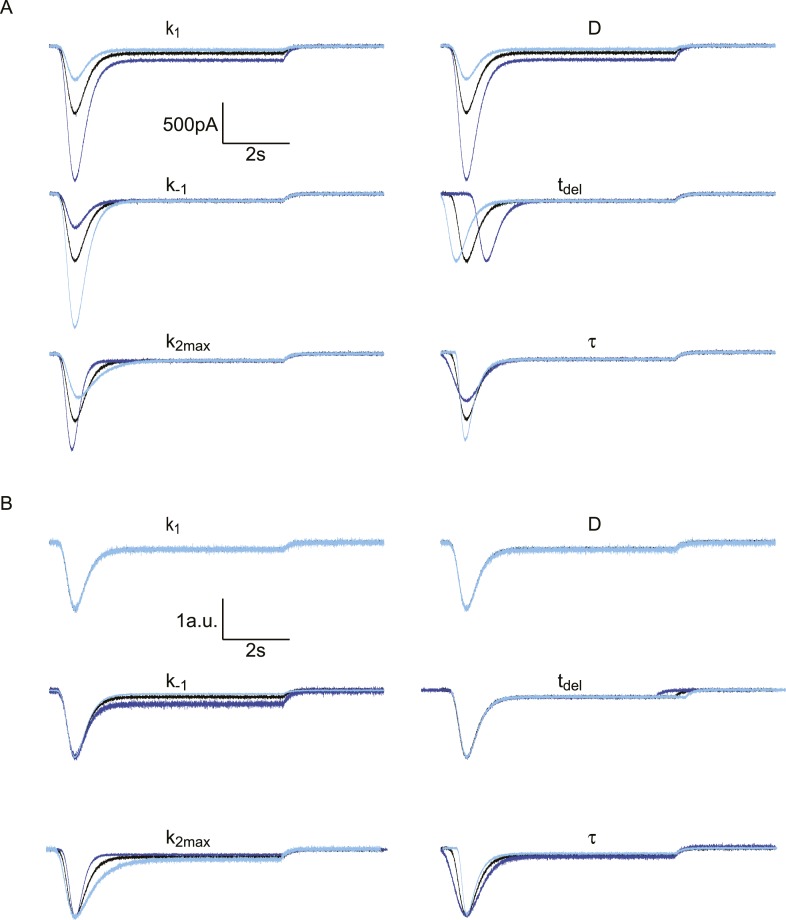
Figure 2. Modelling HS-induced EPSCs.
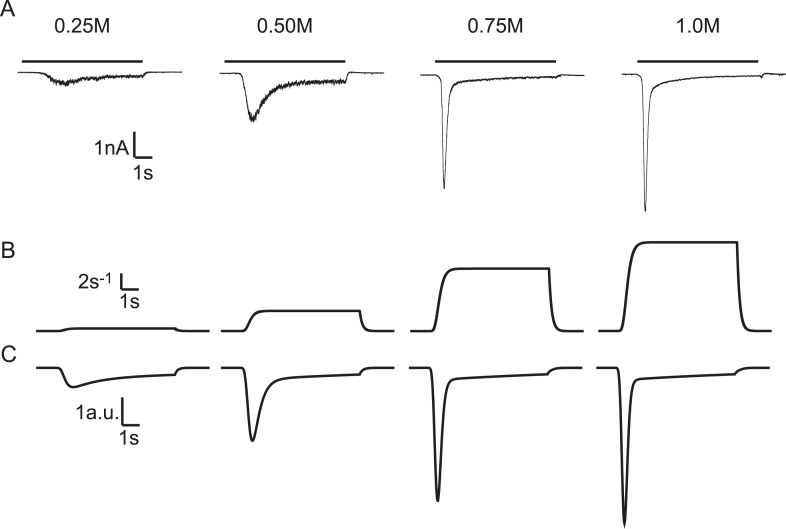
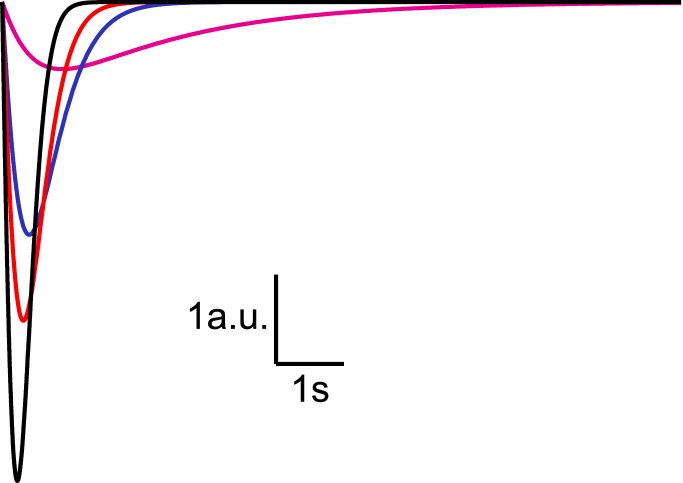
(A) Concentration dependence of HS-induced release kinetics. (B) Model simulations of time courses of k2, for different values of k2,max and (C) corresponding synaptic responses (−k2R).
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05531.004