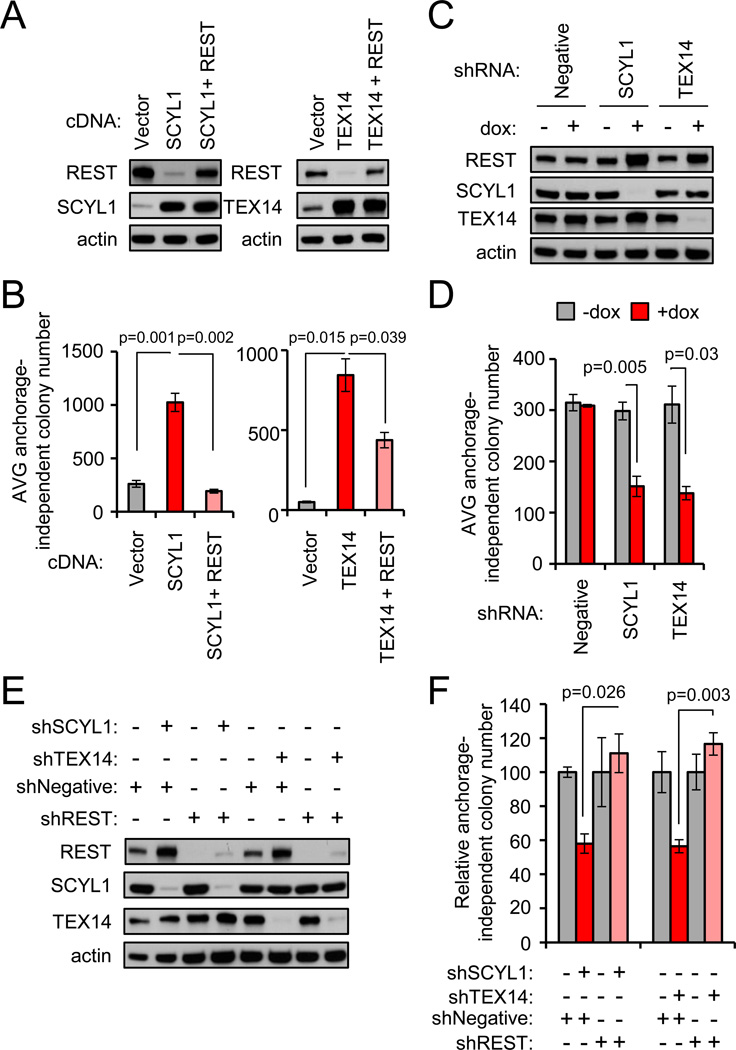
Figure 5. The STP axis supports the transformed state of breast cancer by restraining REST.
- Ectopic SCYL1 and TEX14 reduce endogenous REST protein abundance. BT549 TNBC cells were transduced as indicated and analyzed by western blot.
- SCYL1 and TEX14 promote cellular transformation in a REST-dependent manner. Anchorage-independent growth was assessed in the cells from A. Data presented as mean +/− SE.
- SCYL1 and TEX14 loss of function increases REST protein abundance. MDA-MB231-LM2 TNBC cells were engineered with the indicated dox-inducible shRNAs. Protein levels were assessed by western blot analysis.
- SCYL1 and TEX14 loss of function suppresses cellular transformation. Anchorage-independent growth was assessed in the cells from C +/−dox. Data presented as mean +/− SE.
- SCYL1 and TEX14 support the transformed state by restraining REST. MDA-MB231-LM2 TNBC cells engineered with the indicated dox-inducible shRNAs (from C) were transduced with a constitutive control or REST shRNA retrovirus. Protein levels were assessed by western blot.
- SCYL1 and TEX14 support the transformed state by restraining REST. Anchorage-independent growth was assessed in the cells from E +/−dox. Data presented as mean +/− SE.