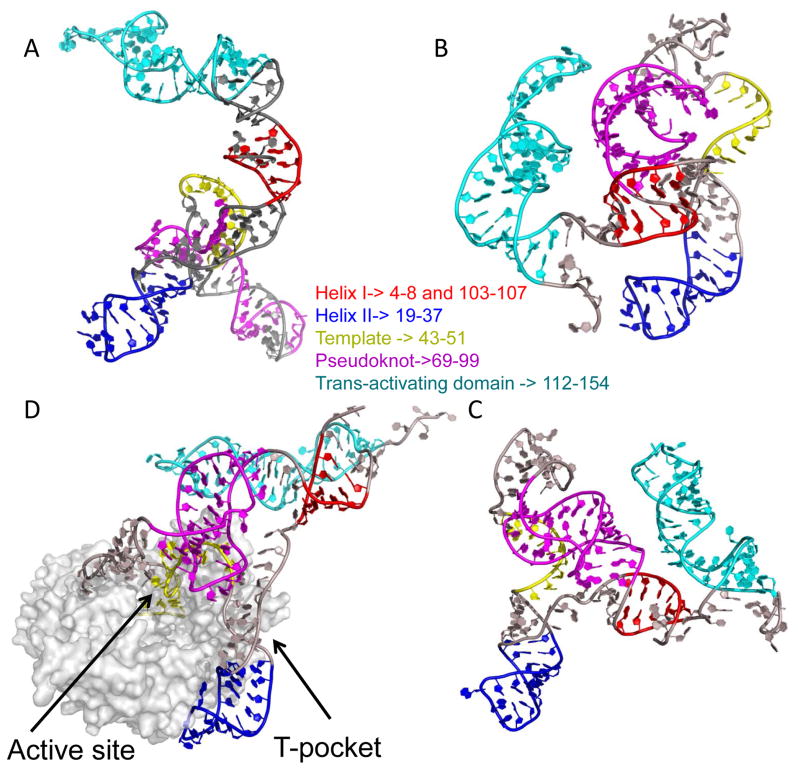
Figure 6.
Conformations of tTER free in solution and bound to tTERT. tTER was modeled using DMD simulations using constraints describe in the Methods section. (A) Unbound tTER. (B) and (C) The two most extreme populations of tTER bund to tTERT predicted by DMD. (C) Was the most populated state. (D) The structure of tTER predicted by DMD when docked to a homology model of tTERT. The TEN domain and flexible linker to the reverse transcriptase domain of TERT was not modeled. Three DNA substrate nucleotides buried within the active site in very close proximity to the catalytic triad of aspartates are colored yellow. The T-pocket of the RNA binding domain of tTERT is indicated. All tTER models are aligned along stem IV nucleotides. Telomerase RNA is shown with stem I nucleotides colored red, stem II nucleotides colored blue, template nucleotides colored yellow, pseudoknot nucleotides colored magenta, and stem IV nucleotides colored cyan. All remaining nucleotides are colored gray.