Fig 7. In hypoxia, HIF-1α is a direct transcriptional repressor of TM9SF4 in leukemic cells.
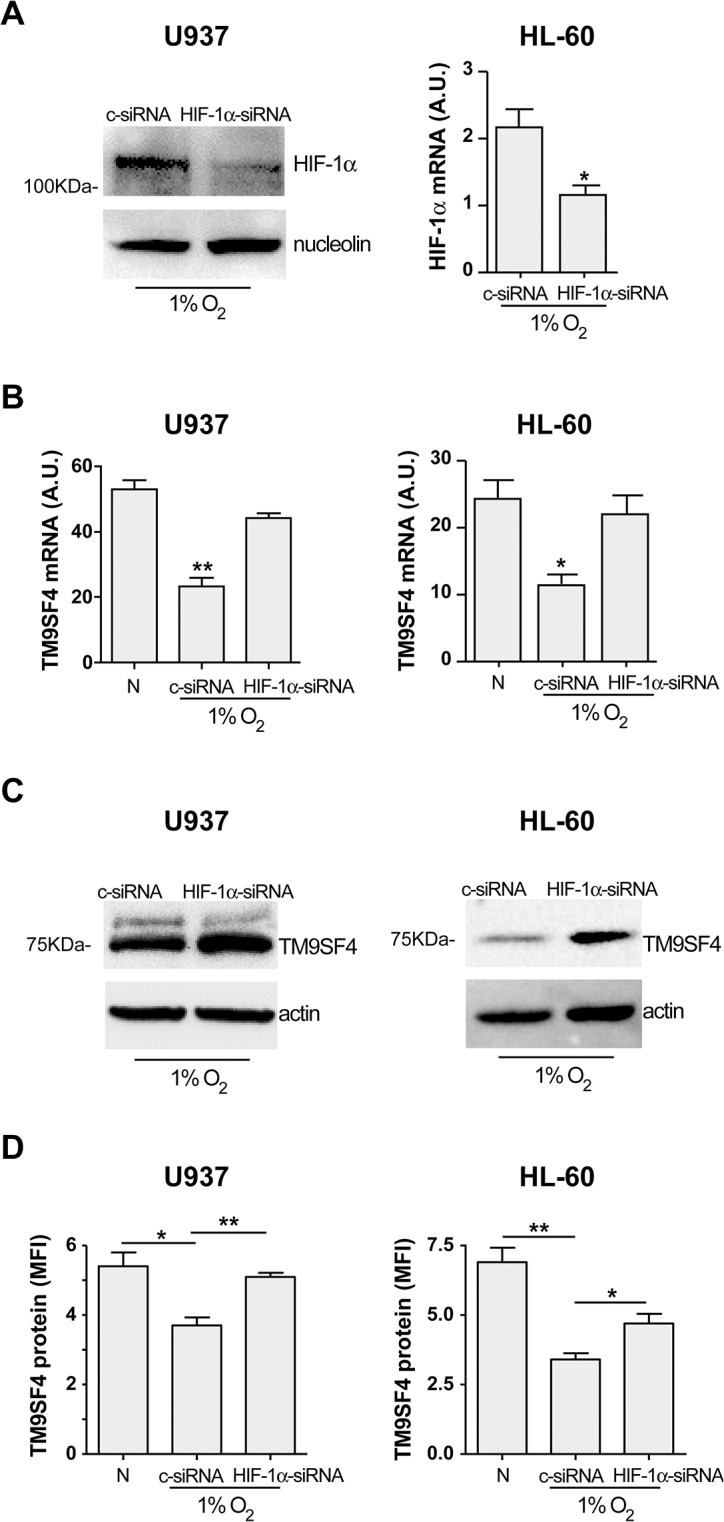
(A) Performed under hypoxic condition (1% O2), knockdown of HIF-1α in U937 and HL-60 cells by using HIF-1α small interfering RNAs (HIF-1α-siRNA), as compared to control siRNA (c-siRNA), was controlled at protein level by Western blot analysis in U937 cells (left panel) and at mRNA level by real time PCR analysis in HL-60 cells (right panel). (B-D) TM9SF4 expression in U937(HIF-1α-siRNA) and HL-60(HIF-1α-siRNA) cells, as compared to U937(c-siRNA) and HL-60(c-siRNA) control cells, cultured in hypoxia (1% O2) compared to normoxia (N), was analyzed at mRNA level by real time PCR analysis (B) and at protein level by western blot (C) and flow cytometry (D) analysis in U937 and HL-60 cells. (A HL-60, B, D) The results of three independent experiments (mean ± SEM values) are shown; *, ** are p<0.05, p<0.01 respectively. (A U937, C) One representative experiment out of three is shown; nucleolin is used as an internal control of U937 nuclear protein extracts; actin is shown as internal control of total protein extracts (C).
