Figure 1.
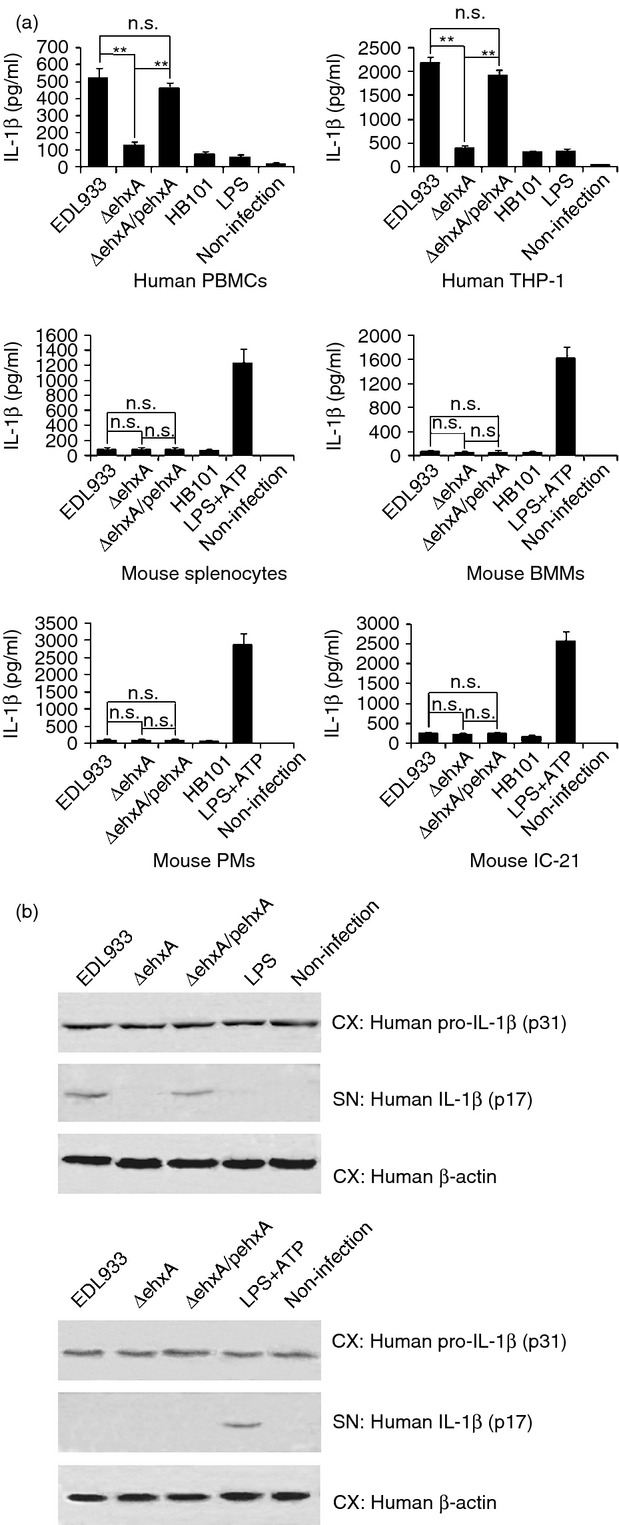
Effects of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 enterohaemolysin on the production of interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), differentiated human THP-1 cells, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -primed (1 μg/ml, 2 hr) mouse splenocytes, peritoneal exudate cells (PMs), bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) and IC-21 cells were infected with EDL933 wild-type (WT), ΔehxA or ΔehxA/pehxA for 4 hr. LPS-primed mouse cells treated with ATP (5 mm, 1 hr) served as positive controls. The commensal E. coli HB101 served as a comparison strain. (a) The concentration of IL-1β in the supernatants was determined by ELISA. (b) The amount of IL-1β p17 and p31 in cell extracts (CX) and supernatants (SN) were visualized by Western blotting. (a) The results represent the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. Significant differences (**P < 0·01) are indicated. n.s., not significant (P > 0·05).
