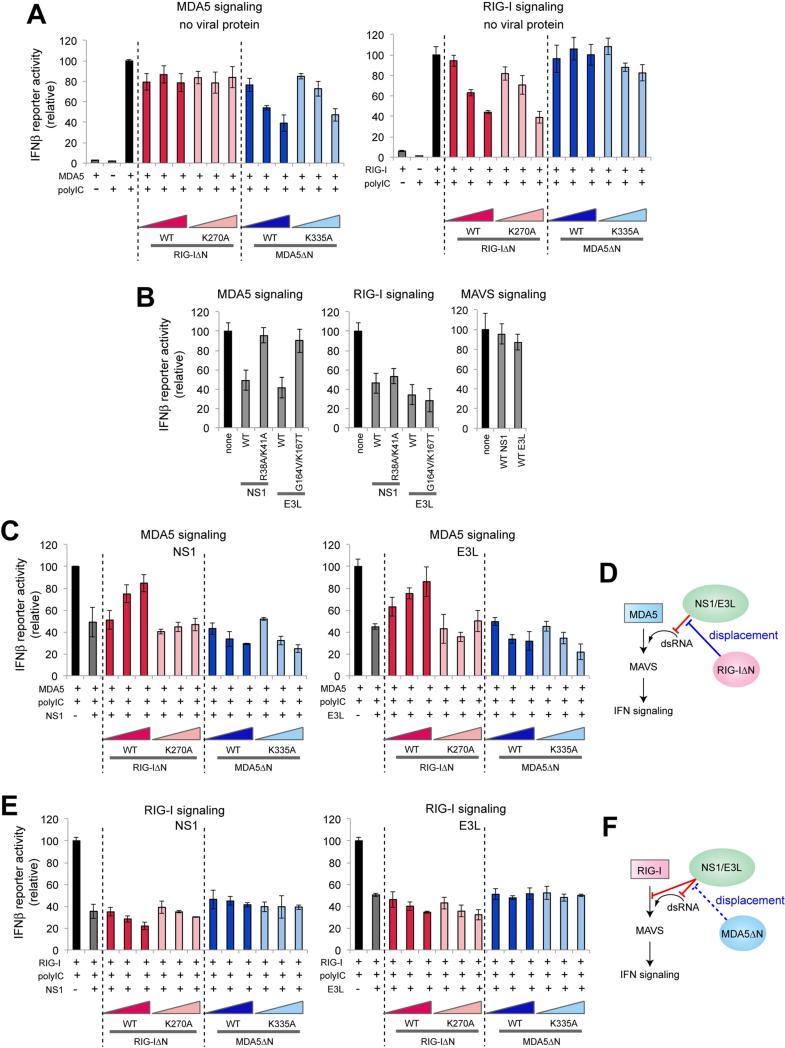
Figure 3.
RIG-IΔN relieves the viral suppression of the MDA5 signaling activity.
A. Impact of RIG-IΔN or MDA5ΔN on the IFNβ reporter activity of full-length MDA5 or RIG-I in the absence of viral proteins. Wild-type (WT) and their catalytic mutants, K270A (for RIG-I) and K335A (for MDA5), were compared. Data are shown in mean ± SD (n=3).
B. Impact of full-length NS1, E3L and their RNA-binding defective mutants on the signaling activities of MDA5, RIG-I and MAVS. See Figure S3E for western blot analysis.
C. Impact of RIG-IΔN or MDA5ΔN on the IFNβ reporter activity of full-length MDA5 in the presence of NS1 or E3L. Data are shown in mean ± SD (n=3).
D. Model in which RIG-I indirectly promotes the MDA5 signaling activity by displacing NS1/E3L from dsRNA.
E. Impact of RIG-IΔN or MDA5ΔN on the IFNβ reporter activity of full-length RIG-I in the presence of NS1 or E3L. Data are shown in mean ± SD (n=3).
F. Model in which the RIG-I signaling activity is affected by NS1/E3L and MDA5ΔN. NS1/E3L suppress RIG-I through both RNA-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Accordingly, the inhibitory effect of NS1/E3L on RIG-I could not be relieved by the protein displacement activity of MDA5.