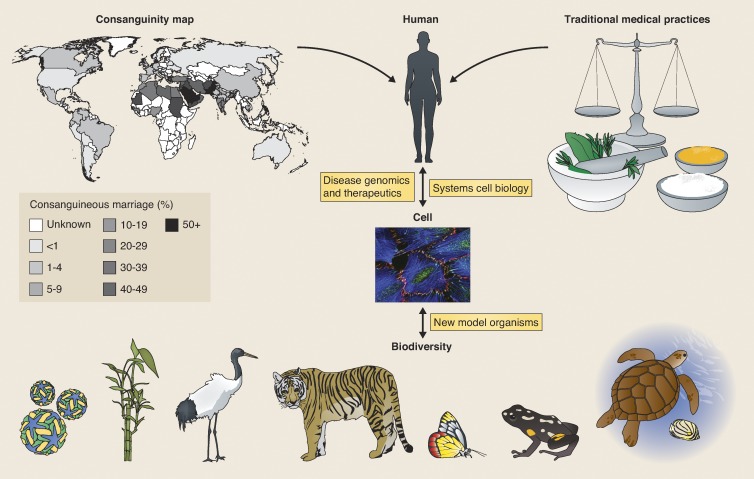
Figure 1.
Expanding the geographical distribution of research activities will broaden the scope of cell biology. Note that the regions in which research in cell biology is likely to grow are areas where consanguinity rates in human populations are very high (notably in India and some parts of China; map adapted from Bittles and Black, 2010; © Bittles and Black) and are located in regions of high biodiversity (biodiversity hotspots; Wilson, 1999). Both in India and China, traditional medical practices are also very prevalent, and their cellular and molecular bases are now becoming amenable to modern biological analysis. Robust and locally connected research will surely be influenced by these geographical attributes, contributing to new understanding of the genetic basis for drivers of diseases, new opportunities for therapeutics, and uncovering the cell biology of novel model organisms. Micrograph courtesy of Stephan Huveneers.