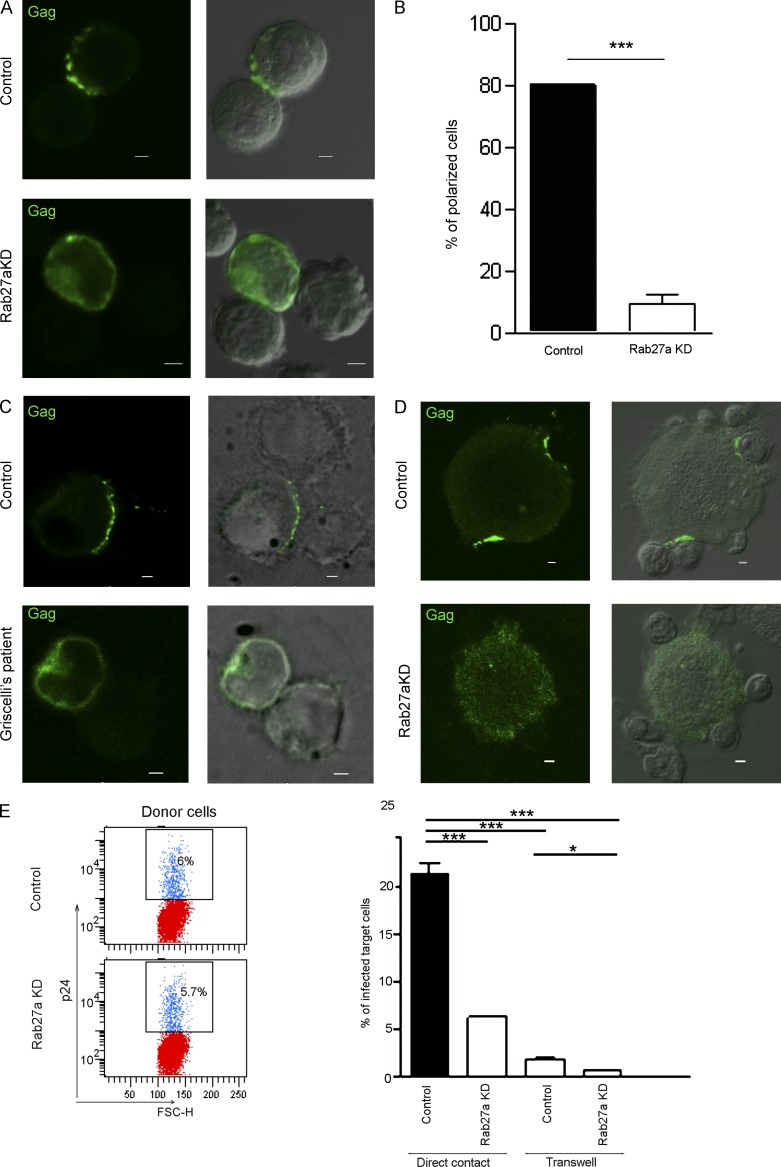
Figure 5.
Formation of the virological synapse and cell-to-cell transmission of HIV are impaired in Rab27a-deficient cells. (A) Control or Rab27a-silenced Jurkat cells were infected with HIV (IIIB strain). At day 7 p.i., cells were plated onto poly-l-lysine–coated coverslips and incubated with noninfected target Jurkat cells for 1.5 h. Gag was stained with anti-p24 antibodies and polarization of Gag at the virological synapses was evaluated by LSCM. Representative confocal and DIC images are shown. (B) Quantification of the number of cells showing a polarized distribution of Gag (30 cell conjugates from two independent experiments). (C and D) The ability of primary CD4+ T cells from a GS patient and the corresponding healthy control (C) and Rab27a-silenced or control MDMs co-cultured with autologous CD4+ T cells to form virological synapses (D) was also evaluated by 3D deconvolution fluorescence microscopy and LSCM, respectively. Representative confocal and DIC images are shown. In C, a 3D maximum intensity projection of 10 optical sections acquired at 0.2-µm intervals is shown. (E) 4,800 HIV-infected control or Rab27a-silenced Jurkat cells present in a total of 80,000 cells (Donor cells, left) were added to GHOST cell cultures either allowing direct interaction or separated by a 0.2-µm pore filter (transwell). After 1.5 h of co-culture, cells were removed, and the percentage of GFP-positive GHOST cells was determined by FACS analysis 48 h later. FSC-H, forward scatter height. The boxes contain GFP-positive cells. Histograms show the means ± SD of three experiments performed in triplicates. *, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. KD, knockdown. Bars, 2 µm.