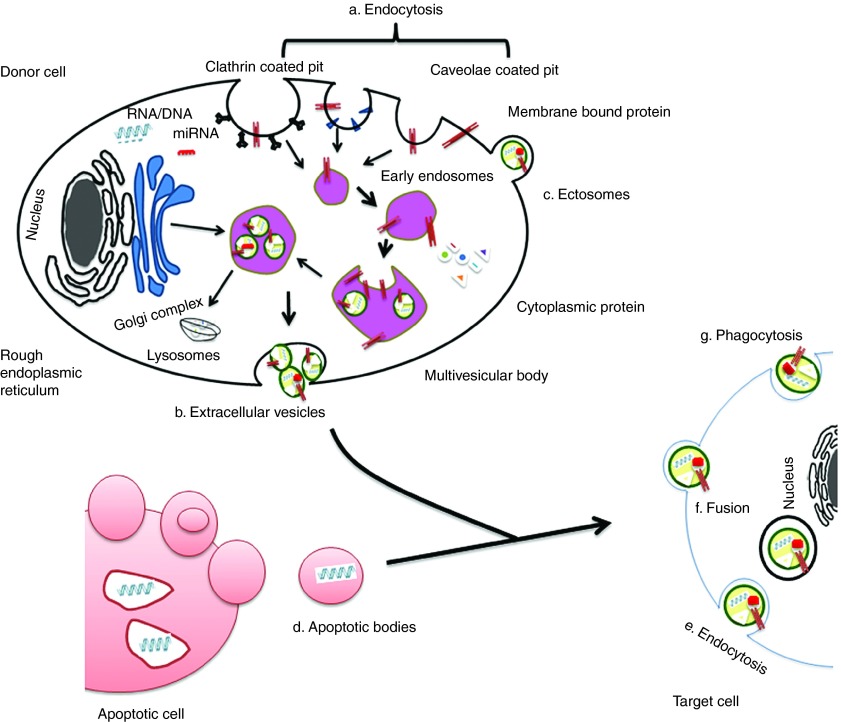
Figure 1.
EVs origin and internalization. Origin of EVs are generally via (a) endocytosis or inward budding of plasma membrane that consist of lipid rafts and is mediated by clathrin-dependent or caveolae-dependent pathway, This gives rise to (b) early endosomes leading to the formation of numerous ILVs within a membrane maturing to MVBs. Finally MVBs fuse with plasma membrane releasing ILVs as exosomes. (c) Ectosomes are vesicles shed from the cell surface and (d) apoptotic bodies are also known as apobodies and are released by cells undergoing apoptosis. EVs are internalized by the target cells through several pathways including (e) endocytosis, (f) fusion, and (g) phagocytosis.