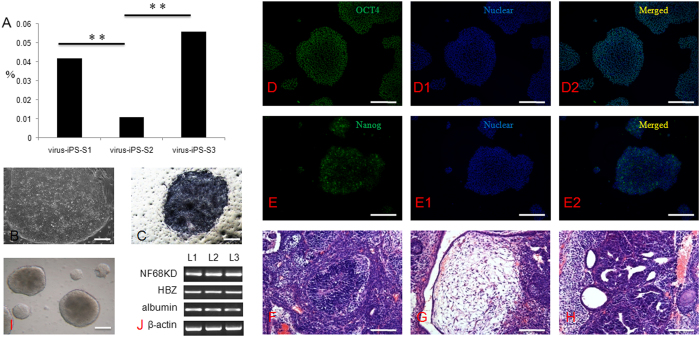
Figure 7.
Derivation and characteristics of iPS cells from different somatic cells. (A) Derivation efficiency was significantly decreased when S2 somatic cells were transfected with virus; (B) iPS cell colony on feeder cells; (C) AP activity (Black colony); (D–D2) OCT4 and nuclear staining and merged images; (E–E2) TRA-1-60 and nuclear staining and merged images; (F) Neural rosette (ectoderm) from in vivo differentiated teratoma; (G) Fat tissue (Mesoderm); (H) Primitive gut (endoderm) from in vivo differentiated teratoma; (H) Embryoid body (EB) formation differentiated from ES cells in vitro; (I) Markers in all three germ layers were expressed in EB, including NF68KD (ectoderm), HBZ (mesoderm) and albumin (endoderm). L1, human iPS cells from S1 somatic cells; L2, human iPS cells from S2 somatic cells; L3, human iPS cells from S3 somatic cells.