Figure 4.
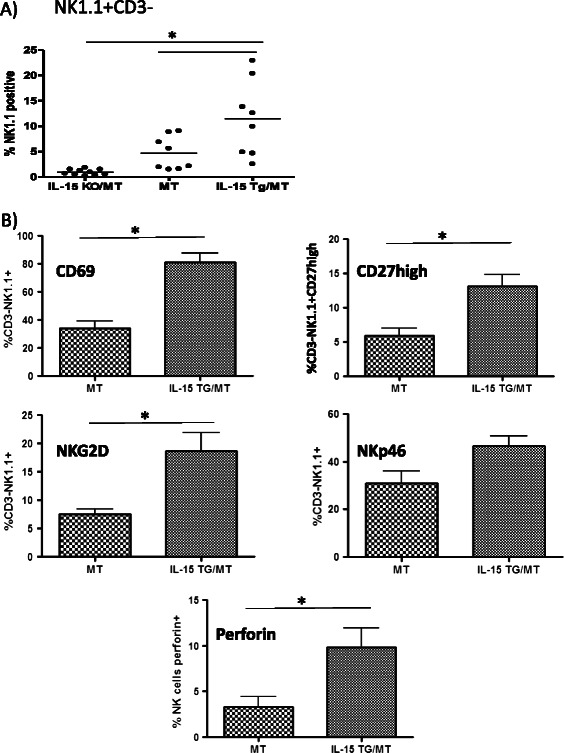
A comparison of NK cell phenotype in IL-15 TG/MT and MT tumors. Tumors from MT, IL-15 KO/MT and IL-15 TG/MT mice were digested and stained for flow cytometry (only one tumor taken from each mouse). (A) Of CD45+ cells in the tumor, there was a higher proportion of NK1.1+ cells in the IL-15 TG/MT tumors than in the MT or IL-15 KO/MT tumors (n = 10- IL-15 KO/MT, 8- MT or IL-15 TG/MT). (B) In the IL-15 TG/MT tumors, the majority of the NK cells possess the early activation marker CD69. In addition, a higher percentage of NK cells in IL-15 TG/MT tumors possess CD27, a marker of highly cytotoxic NK cells. Lastly, a higher percent of the NK cells in IL-15 TG/MT tumors possess the activation markers NKp46 and NKG2D, as well as perforin (n = 3 to 9). *p < 0.05.
