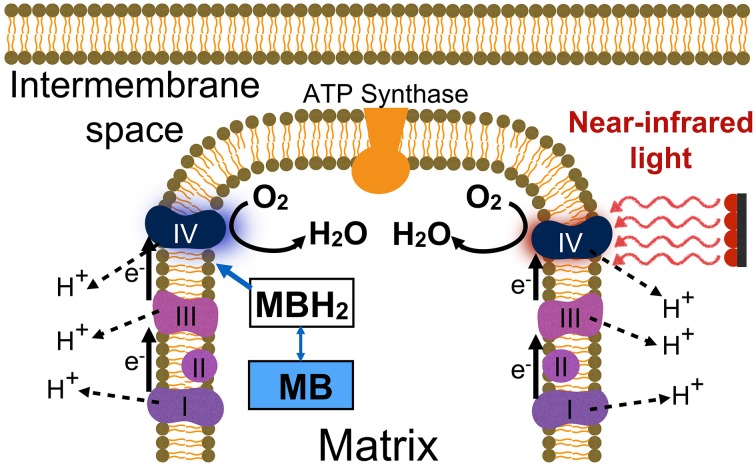
Figure 1.
Two neuroprotective interventions for enhancing mitochondrial respiration. Low-dose methylene blue (MB) acts as an exogenous electron (e-) cycler, boosting oxygen consumption and cell respiration (molecular O2 reduced to H2O). Low-level red-to-near-infrared light directly energizes cytochrome oxidase (Complex IV) via photon absorption, facilitating its catalytic activity and leading to up-regulation of cytochrome oxidase levels. These interventions result in long-term increases in the amount of cytochrome oxidase in the electron transport chain by a process of enzymatic induction, which promotes oxidative energy metabolism and neuronal survival. Abbreviations: I–IV, refer to the four electron transport enzymatic complexes in the inner membrane of mitochondria; MB, is oxidized methylene blue (blue color); MBH2, is reduced methylene blue (colorless); H+, stands for the protons pumped by Complexes I, III, and IV that enter the mitochondrial matrix via ATP synthase, which results in ATP production.