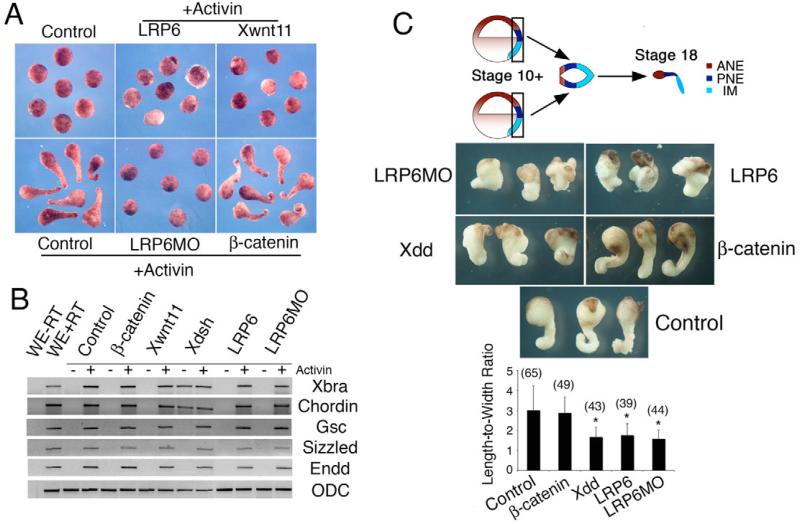
Fig. 2. Loss and gain of Lrp6 function in explants affects convergent-extension movements.
(A) lrp6 mRNA (LRP6; 1 ng) or Lrp6MO (LRP6MO; 40 ng) injections block activin-mediated animal cap elongation, in a similar manner to injection of Wnt11 (400 pg) control. By contrast, injection of β-catenin at levels that cause complete axis duplication (50 pg) has no effect. (B) RT-PCR analysis shows that mesendodermal markers (Xbra, Chordin, Goosecoid, Sizzled, Endodermin) are induced by activin in animal caps and their expression is unaffected by injections of Lrp6MO or lrp6 mRNA. Note induction of Xbra and Chordin after injections of similar amounts of dsh mRNA (1 ng). Loading control: ODC (ornithine decarboxylase). (C) Keller sandwiches elongate when DMZ explants are cultured in apposition. Keller sandwiches injected with Lrp6MO (40 ng) or lrp6 mRNA (1 ng) show impaired elongation (compared to control uninjected or β-catenin expressing explants) and resemble those expressing Xdd (2 ng). ANE, anterior neural ectoderm; PNE, posterior neural ectoderm; IM, involuting mesoderm. Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Asterisks mark differences that are statistically significant from control (P<0.01). Numbers of explants scored are indicated in parentheses.