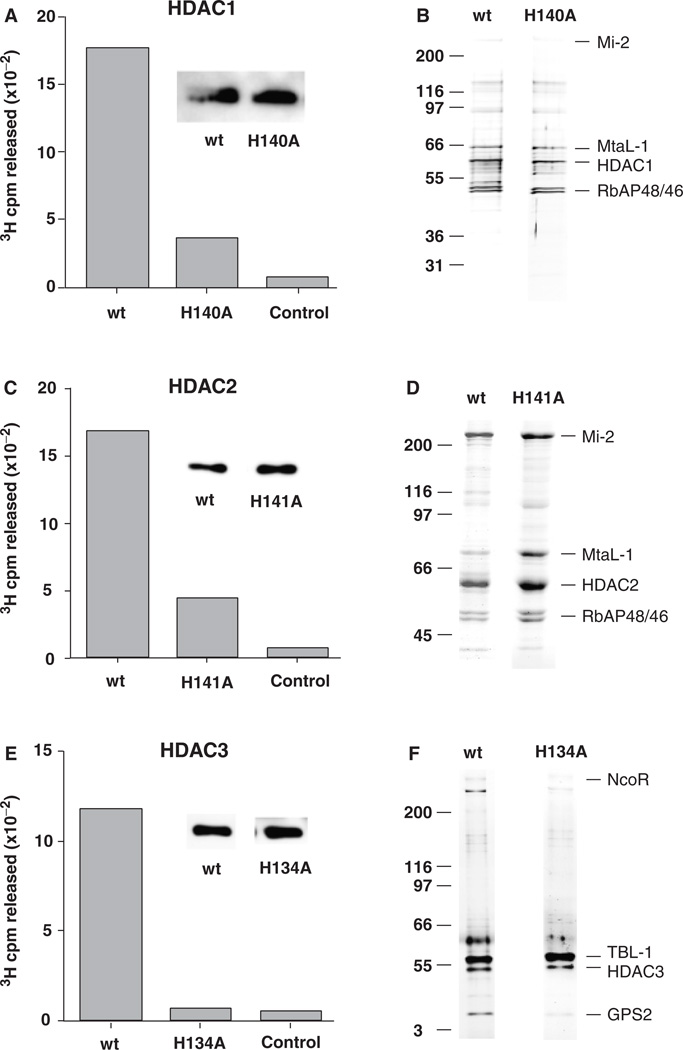
Fig. 2.
Wild-type (wt) and mutant HDACs form similar multiprotein complexes. Flag-tagged HDACs were expressed in Hela cells and isolated using an anti-Flag immunoaffinity adsorbent. HDAC1 enzymatic activity was determined by 3H cpm released from 3H acetate-labeled histones in a 30-min incubation (see “Methods”). (A) Wt, mutant (H140A) HDAC1 complexes isolated from transduced Hela cells; control anti-Flag adsorbent using normal (untransduced) Hela cells. Insets show that similar amounts of Flag-tagged protein were used for each assay. (C) Wt or mutant (H141A) HDAC2 complexes isolated from transduced Hela cells, control anti-Flag adsorbent using normal (untransduced) Hela cells. (E) Wt or mutant (H134A) HDAC3 complexes isolated from transduced Hela cells, control anti- Flag adsorbent using normal (untransduced) Hela cells. Wt and mutant HDACs form similar multiprotein complexes. (B) Comparison of immunopurified Flag-tagged HDAC1 wt and mutant (H140A) multiprotein complexes resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver staining. Right, principal components; left, size markers. (D) Comparison of immunopurified Flag-tagged HDAC2 wt and mutant (H141A) multiprotein complexes. (F) Comparison of wt and mutant (H134A) HDAC3 form similar multiprotein complexes. HDAC, histone deacetylases.