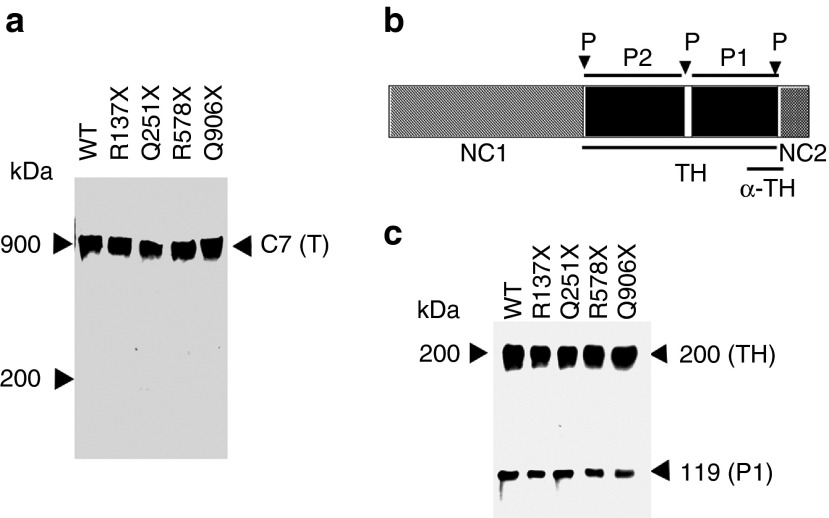
Figure 8.
Aminoglycoside-induced C7 forms stable triple helices. (a) Purified wild-type C7 (C7) and aminoglycoside-induced C7 from four nonsense constructs as indicated were subjected to 4–12% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with a polyclonal antibody to the NC2 domain. Proteins were nonreduced before loading onto gels. The positions of molecular weight markers, and trimer (T) of C7 are indicated. (b) A schematic diagram of the C7 α-chain. The triple helical domain (TH) of C7 contains a 39 amino acid of nonhelical interruption (hinge region). This site of C7 is sensitive to protease digestion, and the helix can be cleaved into carboxyterminal P1 and aminoterminal P2 fragments. Each fragment represents approximately one-half of the TH domain. The protease cleavage sites (P) are indicated by arrows. The recognition region for a polyclonal antibody to the TH domain (α-TH) is also indicated. (c) Purified wild-type C7 (C7) and aminoglycoside-induced C7 from four nonsense constructs, as indicated, were treated with chymotrypsin and analyzed by 6% SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis with a polyclonal antibody to the TH domain. The positions of molecular weight markers, the 200-kDa intact TH domain and the 120-kDa carboxyl-terminal half of the TH fragment (P1) are indicated.