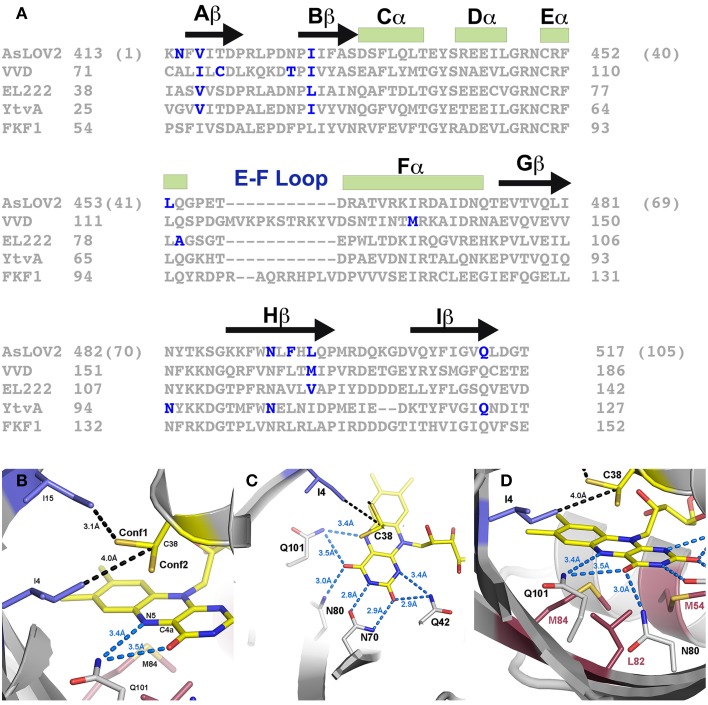
Figure 2.
Sites for rate altering variants. (A) Sequence alignment and universal numbering scheme for LOV proteins and optogenetic tools. The numbering scheme (in parentheses for AsLOV2) used in this review references K413 of AsLOV2 as residue 1 of the core LOV domain. All residues are then numbered in reference to the alignment provided, where residue inserts (E-F loop) or deletions (YtvA) are ignored in the universal numbering system. Residues that have been targeted for rate altering effects are depicted in blue. (B) Steric interactions (blue residues) select for alternative conformations of C38. Conf2 places the thiol directly above the C4a position, where it is poised for C4a adduct formation. I4 juts in between the two conformations placing its methyl group only 4.0 Å away from Cβ. Rotation between the two conformations would require movement of I4. (C) A network of H-bonds in the pyrimidine ring stabilize the C4a adduct through electron withdrawing effects. (D) Full active site containing residues attenuating Conf1/2 (blue), residues at the re-face (red) and H-bonding residues (gray). Three residues, M54, L82, and M84 attenuate adduct decay pathways through steric and electronic regulation of the flavin.