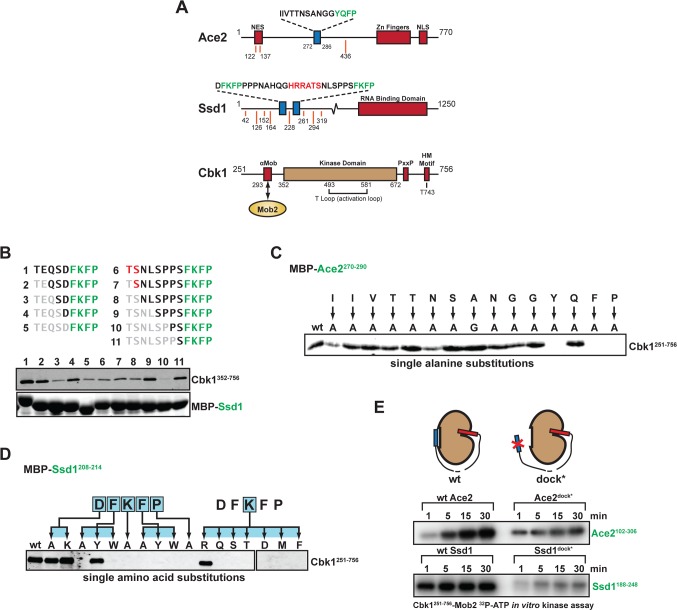
Fig 4. Molecular analysis of Cbk1 docking peptides in Ace2 and Ssd1 highlights importance of a [YF]xFP motif.
(A) Protein schematics with points of interest highlighted. Orange lines denote Cbk1 consensus sites, and blue boxes denote docking motifs. (B) Pulldown of Cbk1 kinase domain by truncated Ssd1 N-terminal (1–5) and C-terminal (6–11) docking motifs suggests that only the FKFP motif is required for interaction. (C) Alanine scan of the Ace2270–290 docking motif suggests that residues N-terminal to the YQFP motif aid in Cbk1 binding. (D) Mutational analysis of Ssd1 N-terminal docking motif highlights the sequence stringency of the core motif and suggests a consensus docking motif of [YF][KR]FP. (E) Cbk1 in vitro kinase assay with Ace2 or Ssd1 fragments containing a phosphorylation site (HxRxx[ST]) and either a WT docking motif (left) or mutated docking motif (dock*, right). Phosphorylation is enhanced in the presence of the WT docking motif.