Fig 6. Docking sites increase robustness of Cbk1 control of in vivo substrates.
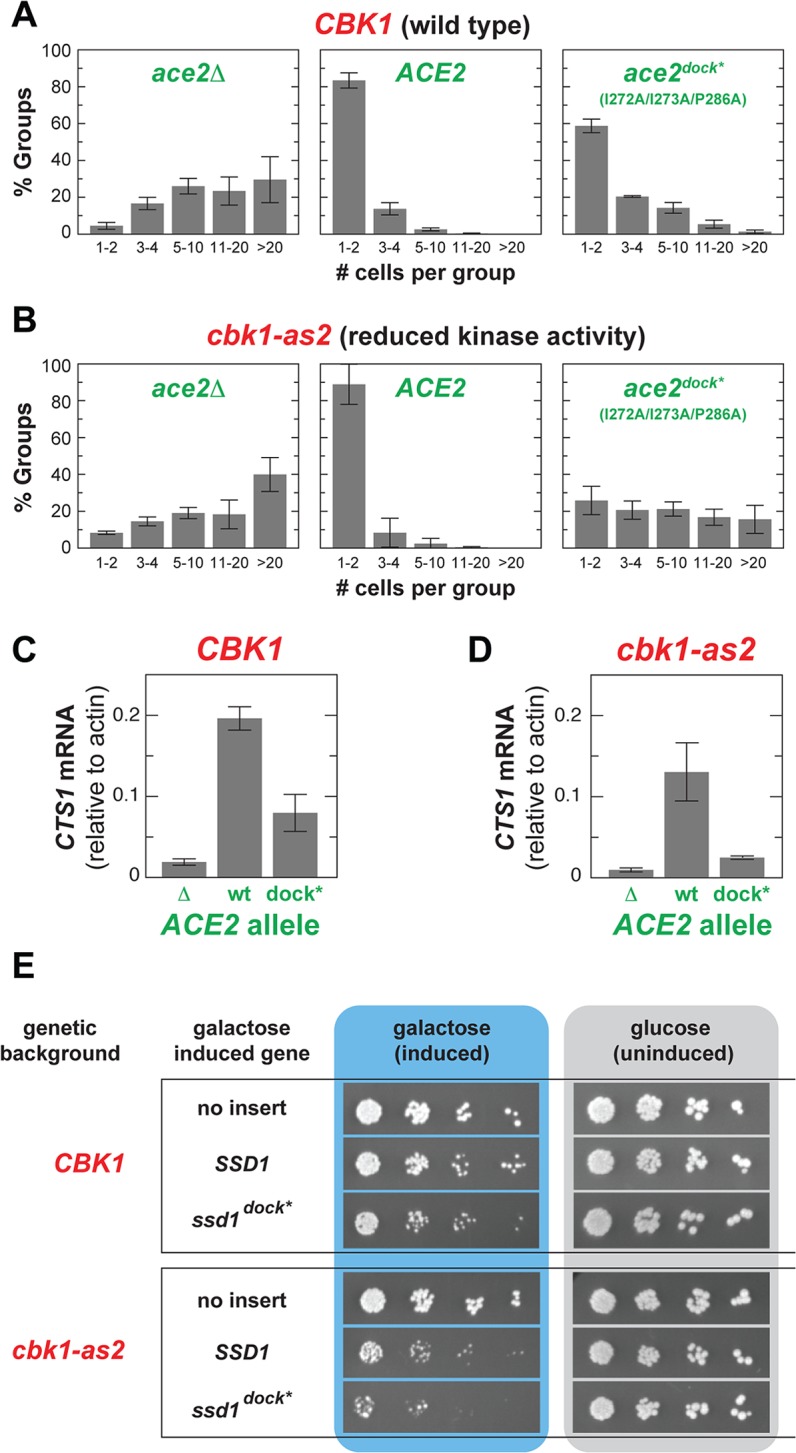
(A) Mutation of the Cbk1 docking motif in Ace2 (ace2 dock*) confers a modest defect in cell separation in cells with WT CBK1. (B) The ace2 dock* allele has a marked cell separation defect in cells carrying the cbk1-as2 allele, which is catalytically weakened. Note that cbk1-as2 cells exhibit no cell separation defect when the WT ACE2 allele is present. (C and D) CBK1 WT cells carrying ace2 dock* have a slight reduction in CTS1 transcript levels (C), while cbk1-as2 cells carrying ace2 dock* exhibit strongly reduced CTS1 transcription (D). (E) Overexpression of the ssd1 dock* allele, carrying mutations that eliminate docking interaction with Cbk1, affects viability of WT cells, and this is far more dramatic in cbk1-as2 cells. Cells were 10-fold serially diluted from left to right and plated on galactose (inducing) or glucose (repressing) media: reduced colony formation in serial dilutions reflects impaired viability. Data for (A) and (B) can be found in S4 Data, and data for (C) and (D) can be found in S5 Data.
