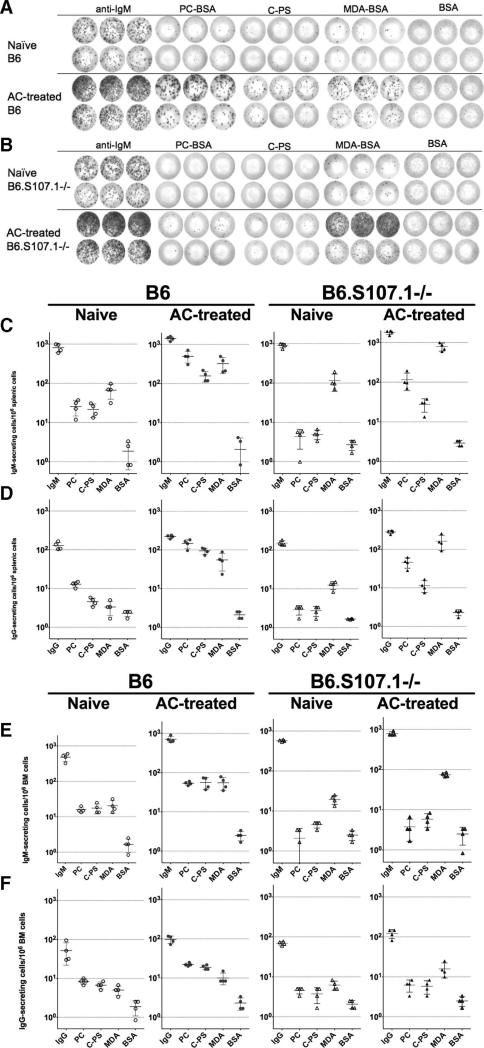
FIGURE 3.
Preferential induction of PC- and MDA-reactive Ig-secreting cells by apoptotic cell treatment. A, Representative ELISPOT results compare splenic IgM-secreting cells from a naive (top) and AC-treated (bottom) adult C57BL/6 (B6) mice, and (B) from congenic homozygotic S107.1-deficient (B6.S107.1−/−) mice. These studies depict results from triplicate wells coated with anti-IgM (total IgM-secreting cells), PC-BSA (PC), pneumococcal C-PS, MDA-BSA (MDA), and BSA (albumin) as the negative control. Each dot represents a distinct Ig-secreting cell after addition of 100,000 (top rows) or 25,000 (bottom rows) splenocytes. Data are depicted for estimated rates of IgM-secreting (C and E) and IgG-secreting cells (D and F) for mononuclear cells harvested from the spleens (C and D) and bone marrows (E and F), with values per million cells presented. Values for individual mice are depicted, with mean values of four mice per group shown as a horizontal bar. Results are representative of two independent experiments.