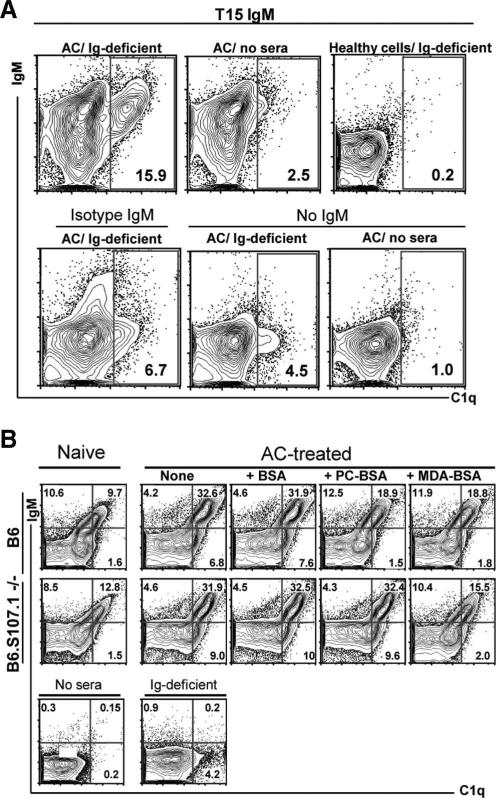
FIGURE 4.
Deposition of C1q onto apoptotic thymocytes is primarily mediated by anti-AC IgM Abs. A, Representative flow cytometric studies demonstrate low but detectable levels of direct deposition of C1q from Ig-deficient sera onto thymocytes undergoing etoposide-induced apoptosis (i.e., ACs), but not to healthy freshly isolated thymocytes (i.e., healthy cells). Apoptosis was confirmed by annexin V staining (not shown). In the presence of T15 IgM, but not isotype control, there is a distinct AC subset with high levels of bound IgM that has a proportionate high level of deposition of C1q. Without Ig-deficient sera there is little or no reactivity with the anti-C1q detection reagent, and the background for the detection signal is demonstrated with an isotype control for the C1q detection in the presence of T15 IgM and sera (not shown). B, Top, Incubation of naive (left) or AC-treated B6 sera (right) results in deposition on AC of IgM and proportionate deposition of C1q primarily in the IgM-associated ACs. While levels are higher with AC-treated B6 sera, IgM and also C1q binding are reduced by preincubation with PC-BSA (PC) or MDA-BSA (MDA) but not by BSA alone. Bottom, Incubation of naive (left) or AC-treated B6.S107.1−/− sera (right) also results in deposition on AC of IgM and C1q, with higher levels of both associated with AC-treated sera. Here, binding of IgM and C1q is reduced by preincubation with MDA-BSA but not by PC-BSA or BSA alone. Results are representative of three independent studies.