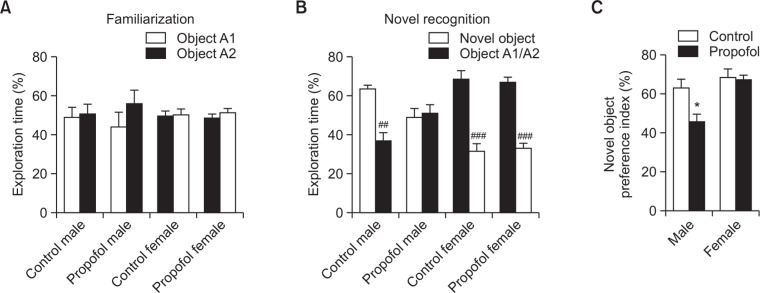
Fig. 7.
Effects of neonatal repeated propofol administration on recognition learning and memory of rats in the novel object recognition test at P42–45. (A) Percentage of exploration time was measured between two identical objects during the familiarization phase. (B) Percentage of exploration time was measured between the novel object and the familiar object during the novel recognition phase. (C) Novel object preference index was calculated by the percentage of exploration time to the novel object from the total exploration time to both objects. Bars indicate the mean ± SEM. Control (male, n=8; female, n=13) and propofol (male, n=10; female, n=16). *p<0.05 vs control male, ##p<0.01 and ###p< 0.001 vs novel object.