Fig 8. Model proposed to explain the requirement for Ku in brc1∆ cells.
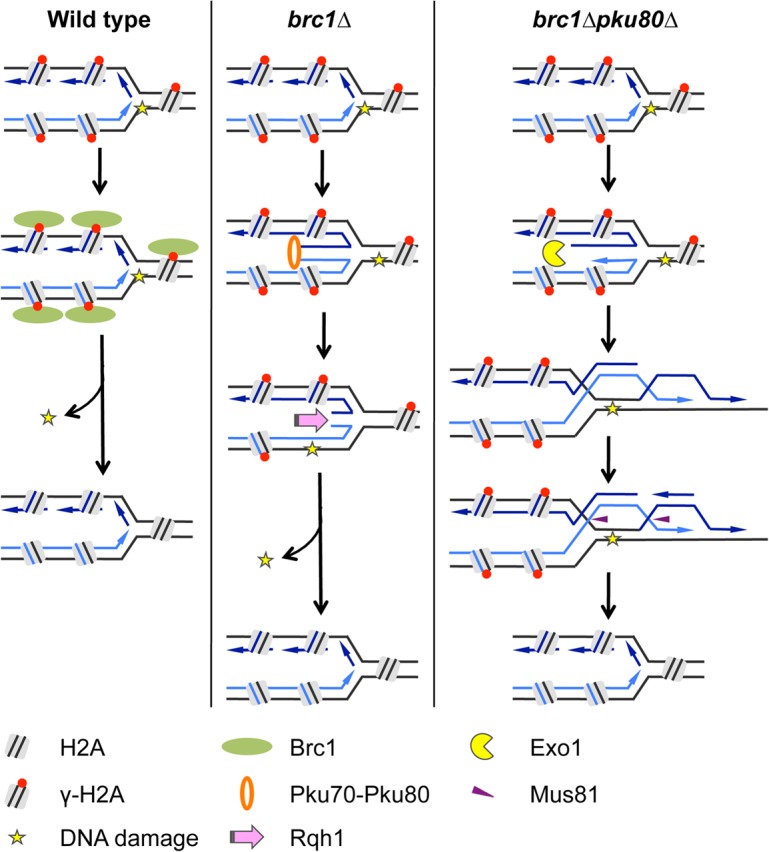
In wild type cells, replication fork stalling leads to phosphorylation of histone H2A followed by recruitment of Brc1, which stabilizes the replication fork. In brc1∆ cells, stalled replication forks are prone to fork reversal. Ku binds the exposed DNA end of the chicken foot structure to prevent fork collapse or rearrangement. This activity of Ku favors resetting of replication fork which increases the likelihood of successful completion of DNA replication. In brc1∆ pku80∆ cells, stalled replication forks undergo homologous recombination without DSB formation as shown or collapse (possibly through a Mus81-dependent mechanism) and reform through homologous recombination (not shown). In either case Mus81-Eme1 is required to resolve Holliday junction-like structures and Exo1 contributes to resection necessary for HR.
