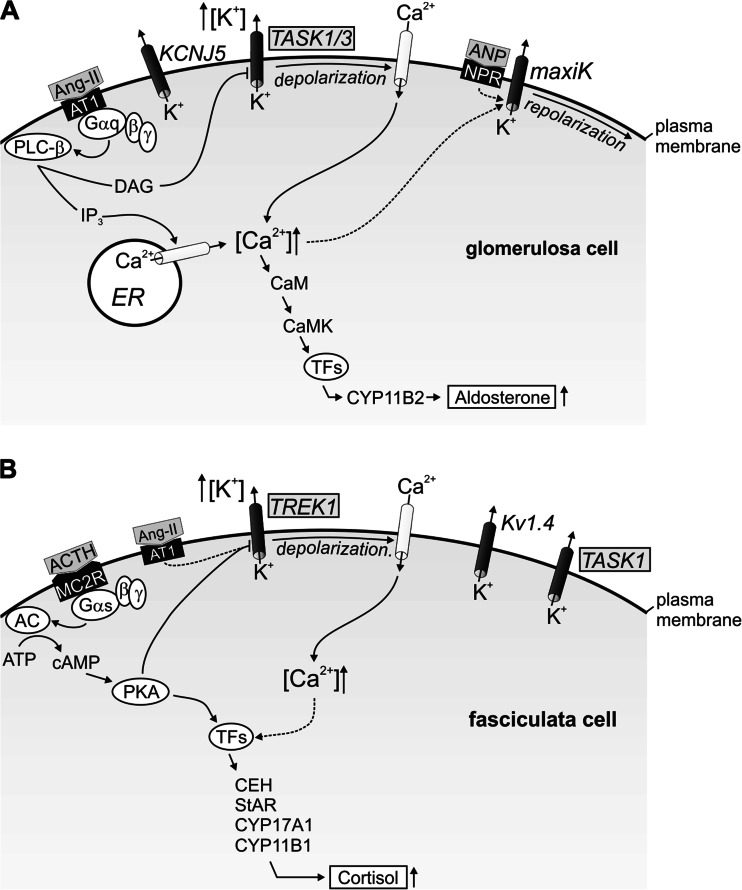
Fig. 1.
Simplified models for the regulation of aldosterone synthesis in zona glomerulosa cells (a) and of cortisol synthesis in zona fasciculata cells (b). a Stimulatory action of Ang-II and increased plasma K+ concentration on aldosterone synthesis depends on membrane voltage depolarization and on increased cytosolic Ca2+. G-Protein-dependent activation of phospholipase-C (PLC-ß) via binding of Ang-II to angiotensin receptor 1 (AT1) leads to generation of inositol-triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 stimulates Ca2+ store release from the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER). DAG-dependent inhibition of TASK1 and TASK3 K+ channels or a high K+-induced shift of the Nernst potential depolarize the membrane. The depolarization activates voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. Ca2+-calmodulin activates CaM-Kinases, and this leads to activation of transcription factors (TFs) and increased transcription of CYP11B2 (aldosterone synthase). MaxiK K+ channels are activated by the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which binds to the natriuretic peptide receptor (NPR), or by increases of cytosolic Ca2+. MaxiK channels repolarize glomerulosa cells and decrease aldosterone synthesis. KCNJ5 K+ channels are highly expressed in human glomerulosa cells, but seem to be inactive under control conditions. b The stimulatory effect of ACTH on cortisol synthesis depends on cAMP-dependent signaling, but also involves membrane depolarization and increased cytosolic Ca2+. ACTH binds to the melanocortic-2-receptor (MC2R) and leads to activation of a Gαs-protein that stimulates adenylate cyclase (AC). cAMP-activated protein kinase A (PKA) activates transcription factors (TFs) inducing transcription of steroidogenic enzymes. These enzymes are required for cortisol synthesis (e.g., CHE: cholesterolester hydrolase, StAR: steroidogenic acute regulated protein, CYP17A1, CYP11B1). PKA also inhibits TREK1 K+ channels, depolarizes the membrane and promotes Ca2+ influx and consecutive activation of transcription factors. TREK1 is also inhibited by Ang-II. Additionally, TASK1 and Kv1.4 K+ channels are expressed in fasciculata cells