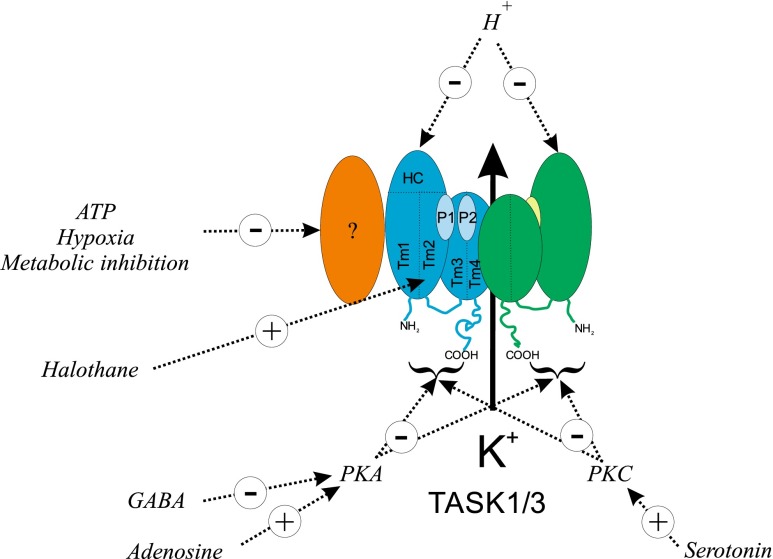
Fig. 3.
Schematic of TASK channel regulation in type 1 cells of the carotid body. Cartoon depicts key regions of the TASK channels including transmembrane spanning domains Tm1, Tm2, Tm3 and Tm4, pore loops P1 + P2, the extracellular helical cap between Tm1 and P1, and N- and C-terminal domains. Hypoxia/metabolic inhibition/cytosolic ATP signalling is presumed to involve some unknown intermediary, e.g. an accessory subunit (?), see text. Modulation by extracellular acidosis probably involves a histidine residue (H98) in the helical cap region (HC). Gaseous inhalational anaesthetics, e.g. halothane, may bind to a region in/near the C-terminal end of the M2 segment [2]. Site of action of the protein kinases PKA and PKC is unknown but is assumed to involve cytoplasmic domains