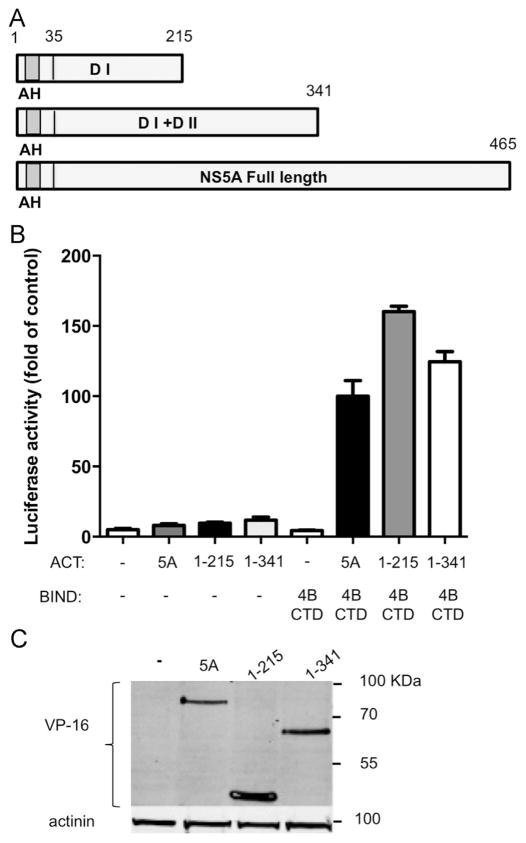
Fig. 5.
NS5A a.a 1–215 are sufficient to mediate its interaction with NS4B. A. Schematic representation of the three NS5A constructs used. The N-terminal amphipathic helix (AH) is labeled in gray; Domain I and II are abbreviated as DI and DII respectively. Amino acid numbers are indicated above. B. The interaction between NS5A domains and NS4B CTD was determined using the two-hybrid system. Full length NS5A, NS5A a.a 1–215 or NS5A a.a 1–341 from genotype 2a were cloned into the appropriate two hybrid vectors. NS4B CTD and NS5A constructs were transfected into Huh7 cells as indicated. The culture media was collected 48 h post-transfection and tested for SEAP activity as a control for transfection efficiency. Followed by a luciferase activity assay preformed on the cell lysates. Luciferase activity results are presented as a percentage relative to the full length NS5A and NS4B CTD value. Values are (mean±SD) from triplicate wells. The graph is a representative result from three independent experiments. Values are (mean±SD) from triplicate wells. C. Expression levels of the NS5A deletion mutants shown in panel A and B. Expression levels were determined in Huh7 cells using western blot with VP16 antibodies. Monoclonal mouse anti- β-actin antibody was used as a loading control. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the right.