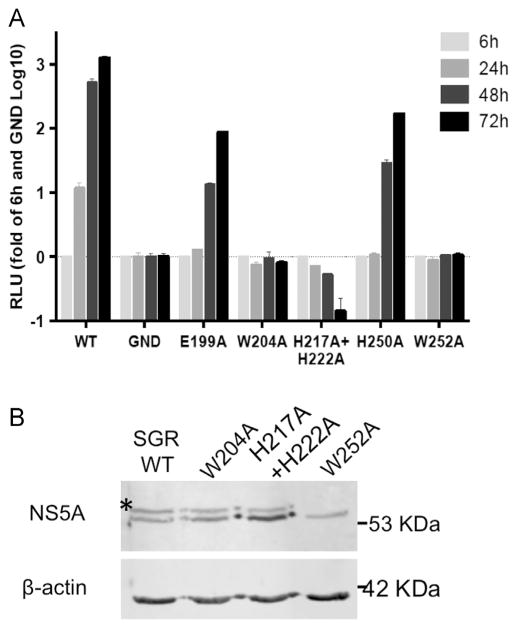
Fig. 7.
Mutations in the C-terminus of NS4B affect HCV replication and NS5A phosphorylation. A. Huh7.5 cells were transfected with in vitro transcribed RNA from a monocistronic reporter virus (J6/JFH(5′C19Rluc2AUbi)) encoding a full-length infectious J6/JFH genome with the Renilla luciferase reporter. Luciferase activity was determined in cell lysates at 6, 24, 48, and 72 h posttransfection. Luciferase activity in relative light units (RLU) is plotted for each time point. The data was normalized to the 6 h values that reflect transfection efficiency and to background luciferase levels determined using a replicon with a mutation in the viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Results represent mean values±SEM from two independent experiments performed in triplicates. B. Expression of pSGR-JFH-1 with the NS4B C terminal mutations using the vaccinia virus infection/transfection system. Huh7 cells were infected with a T7 polymerase expressing modified vaccinia virus, followed by transfection with the indicated pSGR DNA. To monitor the NS5A phosphorylation status, the cells were lysed 20 h post-transfection and analyzed by western blot using the 9E10 anti-NS5A monoclonal antibody. Monoclonal mouse anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control. Shown is a representative blot from 2 independent experiments. Asterisk indicates the hyperphosphorylated form of NS5A. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the right.