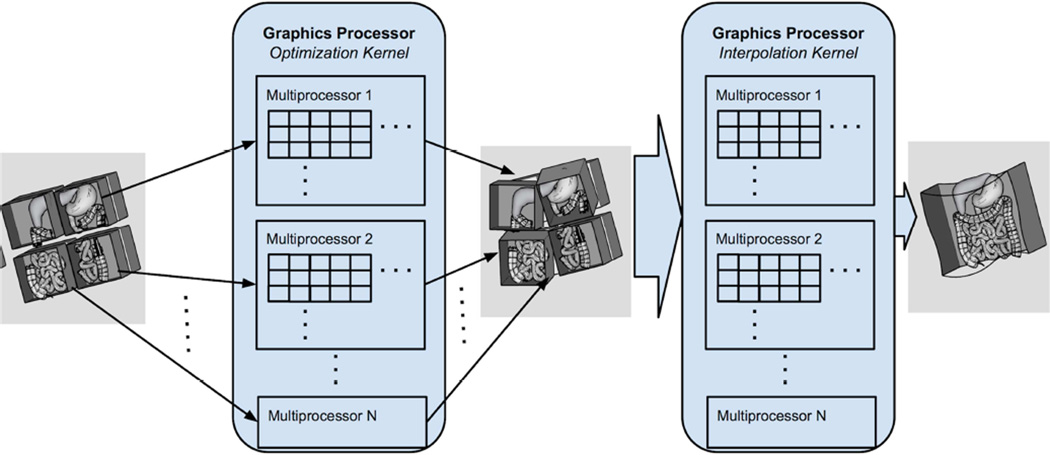
Figure 2.
The nonrigid image registration with image subdivision approach was accelerated in a GPU kernel at both voxel and subvolume levels. A subvolume is assigned to one group of threads, which is executed by a GPU multiprocessor, and a voxel within a subvolume is assigned to a thread, which executes on a single core in a multiprocessor. Once an optimized set of subvolume transformations is found, a resampling GPU kernel takes the transforms of the subvolumes, derives a smooth transformation field, and applies it to the floating image to produce a final registered image. The computation for each pixel is independent, permitting the mapping of each voxel to a single thread.