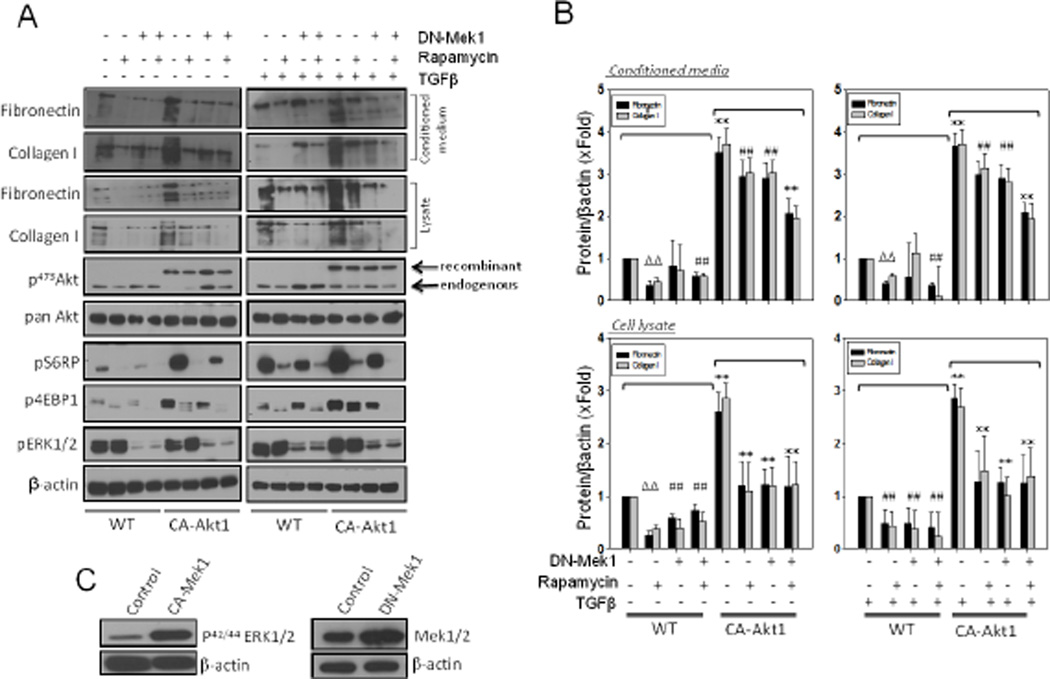
Figure 3. Both Mek1 and Akt1 are important for ECM protein synthesis in fibroblasts.
(A) NIH 3T3 fibroblasts were viral transfected with either CA-Akt1 and/or DN-Mek1 and/or co-treated with 25 µM of Rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor) in serum free medium with or without TGFβ stimulation. After 16 hours, conditioned media were collected, followed by TCA precipitation and cells were lysed using lysis buffer. Precipitated proteins from conditioned media were subjected to Western blot analysis to detect fibronectin and collagen type I, whereas cell lysates were analyzed for changes in the phosphorylation level of the molecules of AktmTOR-cRaf signaling pathways such as: Akt, S6 ribosomal protein, 4EBP1 and ERK1/2. (B) Graph showing changes in the synthesis and secretion of fibronectin and collagen I in cell lysates and conditioned media from cells being either transfected with Ad-DN-Mek1 and/or treated with Rapamycin inhibitor. (C) Western blot images of NIH 3T3 cell lysates transfected with Ad-CA-Mek1 and Ad-DN-Mek1 showing expression of viral expressed proteins. Data presented as mean ± SD (*p<0.001; Δp<0.01; #p<0.05; n=3).