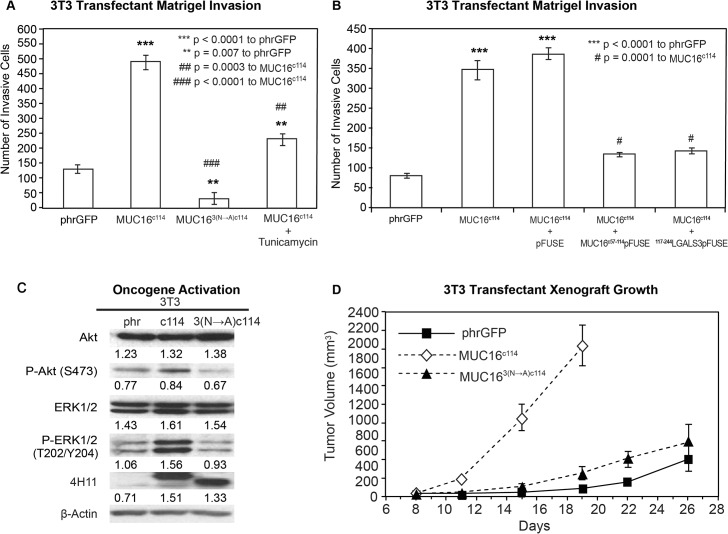
Fig 5. Effect of N-glycosylation on MUC16 transformation.
A) Matrigel invasion assay for 3T3 transfected cell lines, phrGFP control vector or MUC16c114 or MUC163(N—A)c114 and MUC16c114 treated with 0.1 μg/mL Tunicamycin. As seen earlier, MUC16c114 cell lines were significantly different (p<0.0001) than the phrGFP vector control. The MUC163(N—A)c114 cell line was still significantly more invasive (** p = 0.007) compared to the phrGFP vector control. Treatment with the N-glycosylation inhibitor Tunicamycin significantly inhibited matrigel invasion compared to the untreated MUC16c114 (##p = 0.0003), and MUC163(N—A)c114 is highly significant (### = p<0.0001) compared to MUC16c114, suggesting that N-glycosylation is critical for MUC16-induced matrigel invasion. B) Matrigel invasion assay for 3T3 transfected cell lines compared to the phrGFP control vector. 3T3 cells transfected with MUC16c114 were treated with media alone, with 5 μg/mL of control pFUSE hIgG1-Fc2 fusion protein, with 5 μg/mL of MUC16c57-114-pFUSE hIgG1-Fc2 fusion protein, or with 5 μg/mL of 117-244LGALS3-pFUSE hIgG1-Fc2 fusion protein, as detailed in S4 Fig As seen earlier, the MUC16c114 cell line was much more invasive than the phrGFP vector control 3T3 cells (p<0.0001), and this increase in invasion was unaffected by exposure to pFUSE vector only protein. In contrast, MUC16c114 cell line treated with MUC16c57-114-pFUSE hIgG1-Fc2 fusion protein or 117-244LGALS3-pFUSE hIgG1-Fc2 fusion protein demonstrated significant (# p = 0.0001) inhibition of matrigel invasion compared to MUC16c114 control cells. C) Effect of MUC16 expression on ERK/AKT signaling. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (pT202/Y204) and AKT (S473) was increased in the 3T3 transfected with MUC16c114; however, the effect was much diminished in 3T3 cells transfected with the MUC163(N—A)c114 vector. Despite the three asparagine—> alanine mutations, Western blot with the anti-MUC16 antibody, 4H11 mAb, showed a higher signal than either the phrGFP vector control or the native MUC16c114 transfected cells, indicating that the high levels of MUC163(N—A)c114 protein is expressed in the transfected 3T3 cells, and surface expression was confirmed in S2 Fig β-Actin normalized densitometry quantification values are shown below each Western blot in the figure. D) MUC16-positive tumor growth in athymic nude mice. Two million tumor cells were introduced into the flank of 20 nu/nu mice, and the mice were observed for tumor formation. Tumors were measured by calipers twice weekly. The differences in mean tumor volume were significantly greater for mice bearing MUC16c114 tumors (p<0.0001). As seen earlier, 3T3 MUC16c114 transfectant was highly significant at *** p<0.0001 compared to the phrGFP control vector. However, MUC163(N—A)c1143T3 transfectants did not show any significance over phrGFP vector control 3T3 cells, indicating that the mutations of N-glycosylation dramatically decreased in vivo tumor growth and invasion.