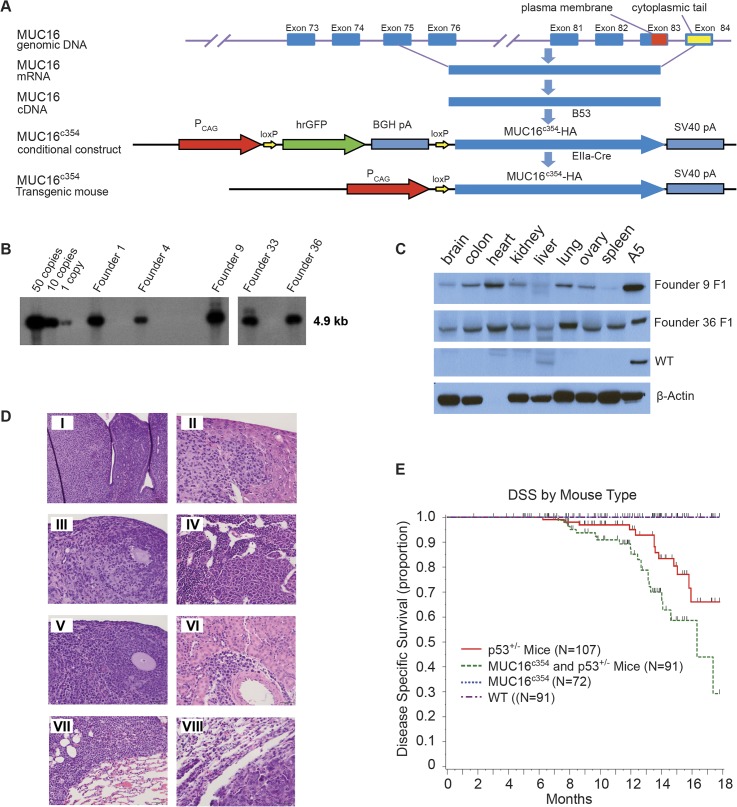
Fig 6. MUC16c354 transgenic mice.
A) Strategy for MUC16c354 conditional construct. A CMV early enhancer plus the chicken β actin promoter (CAG) was used to drive the transcription of hrGFP between two loxPs and the downstream MUC16c354 sequence. B) Southern blot shows 12 candidates of MUC16c354 positive founders among 99 animals after the microinjection procedure. C) Western blot with anti-MUC16c114 4H11 was used to identify founders 9 (~50 copies) and 36 (~10 copies) for MUC16c354 mouse colony development. A5 is a positive control from a stable transfected SKOV3 with MUC16c354. D) Histological analyses of tumors from double MUC16c354:p53+/- transgenic mice. Multiple sarcomas and lymphomas were identified in the double MUC16c354:p53+/- transgenic mice. Sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Tumors included histocytic sarcoma in the uterus (I, Scale bar:100μm), liver (II, Scale bar:50μm), ovary (III, Scale bar:50μm) and bone marrow (IV, Scale bar:50μm); lymphoma in the ovary (V, Scale bar:50μm), kidney (VI, Scale bar:50μm), and lung (VII, Scale bar:50μm); and carcinoma in the lung (VIII, Scale bar:50μm). E) Transgenic mouse cancer-specific Kaplan-Meier survival curves: the MUC16c354 mice (black line) showed no spontaneous tumor development over the first 18 months, similar to the wild type (WT, red dashed line). However, when MUC16c354 mice were crossed with p53+/- mice, the double transgenic MUC16c354:p53+/- mice (green dashed line) showed a significantly worse overall survival due to spontaneous tumor development compared to either the p53+/- mice (red line) (p<0.014) or the MUC16c354 mice. The number of tumors were p53+/- mice 20/107; MUC16c354 and p53+/- Mice 34/91; MUC16c354 1/72; and wild type 0/91.