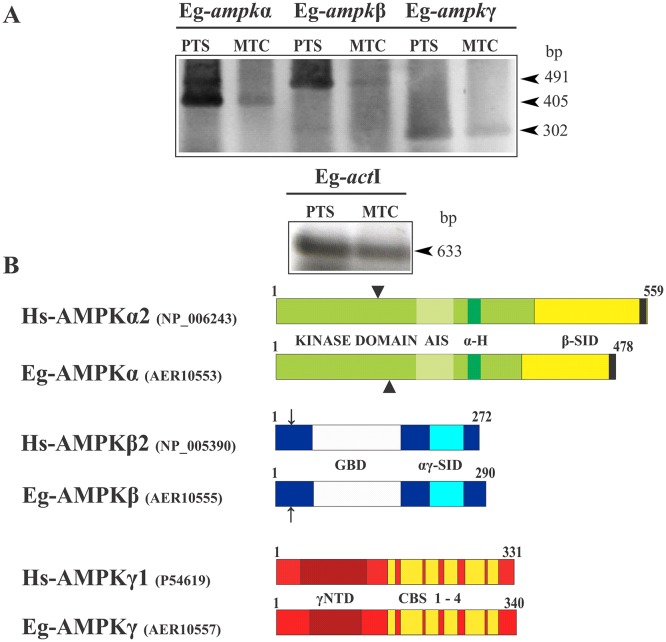
Fig 4. Expression and structural features of the subunits of E. granulosus AMPK.
(A) Reverse transcription-PCR analysis of the three subunits of Eg-AMPK (α, β and γ) from total RNA of protoscoleces (PTS) and metacestodes (MTC). Amplification of Eg-actI was used as a loading control. Molecular sizes of amplicons are indicated with arrowheads. (B) Schematic representation of Homo sapiens AMPKα1, AMPKβ2 and AMPKγ1, and of the predicted AMPK protein from the E. granulosus genome. Identification of kinase domain, β-subunit interaction domain (β-SID), autoinhibitory sequence (AIS), α-hook (α-H) and nuclear exportation sequence (black box) in the catalytic subunit; glycogen-binding domain (GBD) and α- and β-subunits interaction domain (αγ-SID) in the β-regulatory subunit; and divergent N-terminal domain (γNTD) and cystathionine-beta-synthase repeats (CBS 1–4) in the γ-regulatory subunit.