Figure 4.
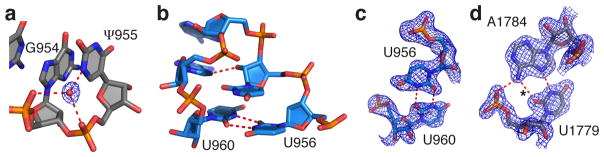
Pseudouridines and syn-pyrimidines in the ribosome. (a) Pseudouridine with a major groove water molecule. Shown is the N1 imino group of ψ955 in 23S rRNA hydrogen bonding to a water molecule that in turn hydrogen bonds to the non-bridging phosphate oxygen of ψ955 and G954. The feature enhanced map is contoured at 2.5 standard deviations from the mean. (b–d) Examples of syn-pyrimidines in the ribosome. Nucleotide U960 in a syn conformation stabilizes a triloop capping helix h31 in 16S rRNA by forming a reverse U-U base pair with U956. (c) The feature enhanced map for the U960–U956 base pair is contoured at 2.5 standard deviations from the mean. (d) Nucleotide U1779 in 23S rRNA adopts a syn conformation to form an unusual reverse Hoogsteen A–U base pair with A1784, allowing the N6 exocyclic amino group of A1784 to hydrogen bond with a non-bridging phosphate oxygen of U1779. The feature-enhanced electron density map is contoured at 2.5 standard deviations from the mean. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by red dashed lines. The hydrogen bond marked with an asterisk is 3.3 Å long.
