Figure 5.
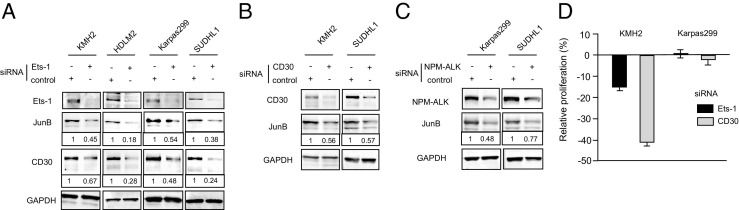
Interrelationship among Ets-1, JunB, CD30, and NPM-ALK in HL and ALCL cell lines. A: Ets-1 knockdown reduced the expression of JunB and CD30 in HL and ALCL cell lines. Immunoblot analyses of Ets-1, JunB, and CD30 after 24 hours of Ets-1 knockdown were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Whole cell lysate, 30 μg, was used for each analysis. The level of expression of JunB and CD30 in cells treated with Ets-1 or control siRNA was measured using densitometry. Values were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Protein expression levels in cells treated with Ets-1 siRNA are expressed relative to those treated with control siRNA, which were set at 1. B and C: CD30 or NPM-ALK knockdown reduced the expression of JunB in HL and ALCL cell lines. Immunoblot analyses of JunB, CD30, and NPM-ALK 24 hours after CD30 or NPM-ALK knockdown was performed as described in Materials and Methods. In the KMH2 HL cell line, only CD30 was knocked down (B), whereas in the ALCL cell lines, CD30 and NPM-ALK were knocked down by their respective siRNA (B and C, respectively). Whole cell lysate, 30 μg, was used for each analysis. The expression levels of JunB in cells treated with CD30 or NPM-ALK siRNA relative to controls were calculated as described as in A. D: Cell proliferation analysis after Ets-1 and CD30 knockdown. The KMH2 HL and the Karpas299 ALCL cell lines were transduced with Ets-1, CD30, or control siRNAs, and their proliferations were determined by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assays. Proliferation levels in cells treated with Ets-1 or CD30 siRNA are expressed relative to those treated with control siRNA, which were set at 100%. The results are presented as reduction rates. Data are given as the mean ± SD of more than three triplicate experiments.