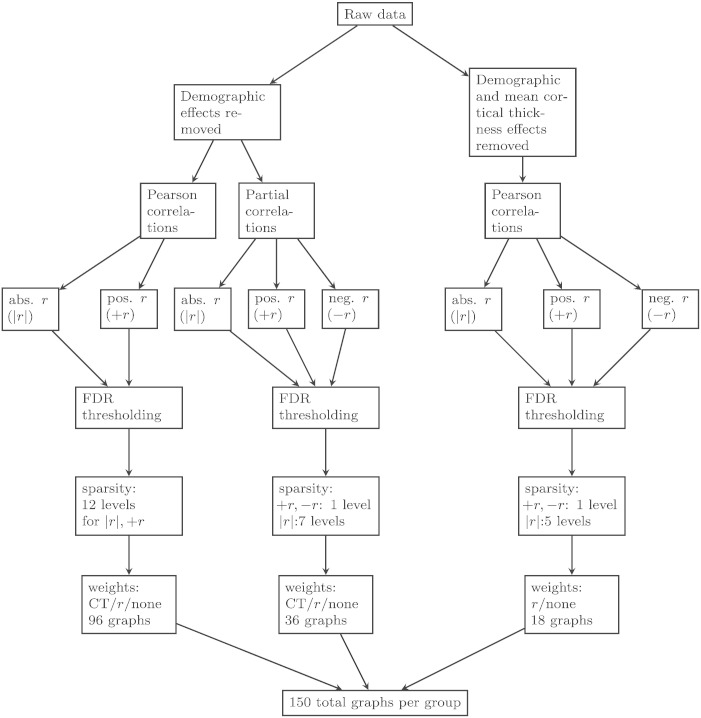
Fig. 1.
This figure depicts the different graph creation methods. Starting from the raw data, there were two possible linear regressions used, one of which controlled for mean cortical thickness and both controlled for the demographic effects of age, gender, and education. For the latter regression, either Pearson or partial correlations were calculated whereas only Pearson correlations were used when the effect of mean cortical thickness was removed. Then, an FDR thresholding was applied to determine significant edges on (1) absolute r-values, (2) positive r-values only, or (3) negative r-values. Then sparsity thresholding was applied at various levels. Finally, edge weights were applied (uniform, r-values, or cortical thickness).