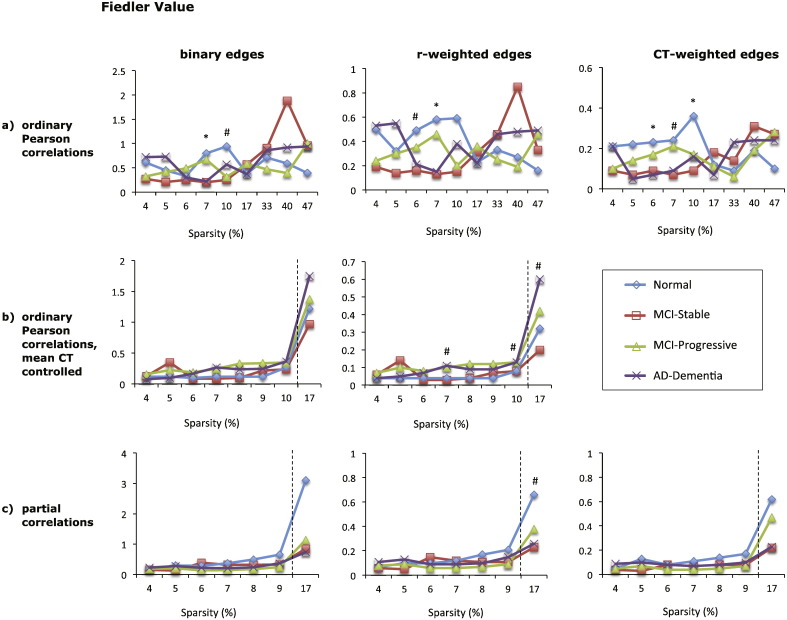
Fig. 6.
Mean Fiedler value of eight types of cortical networks for the four diagnostic groups. The Fiedler value of graphs based on absolute Pearson correlations is shown in (a), top row, for graphs based absolute Pearson correlations with mean cortical thickness controlled in (b), middle row, and for graphs based on absolute partial correlations in (c), bottom row. Each column shows the results for graphs with different edge weights: binary edges (left column), correlation-weighted edges (middle column), and cortical thickness weighted edges (right column). The x-axis shows the sparsity level (S) at which the Fiedler value was compared across diagnostic groups. For each level of S shown, only edges that met the FDR correction of q < 0.05 were included, except where S = 17% for graphs shown in (b) and (c), where q < 0.1. Significant differences between the normal and AD-dementia groups are indicated as follows: #p < 0.1, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.005 (all p-values two-tailed).