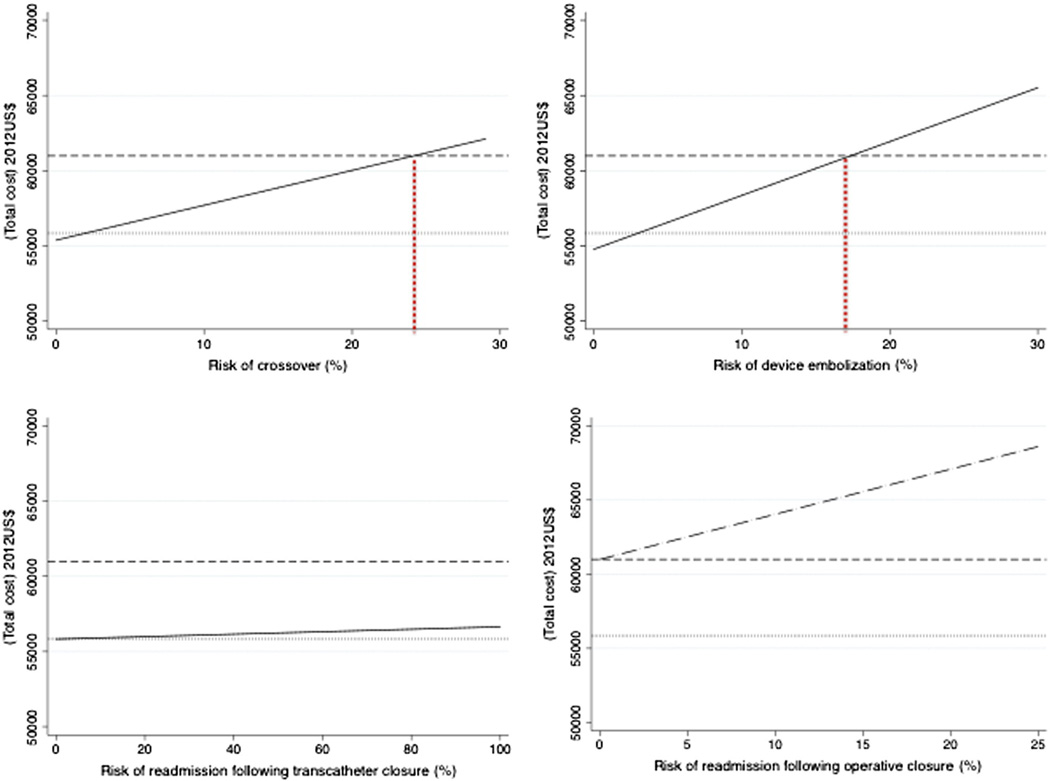
Figure 2.
Effect of crossover, reintervention, and 30-day readmission rates on cost. Graphs depict total cost of closure of ASD (2012 US$) over a range of possible event rates (percentages) for crossover to from transcatheter to operative closure (A), device embolization and repeat catheterization (B), acute care after device closure (C), and acute care after operative closure (D). Adjusted costs of device closure (dotted line) and operative closure (dashed line) are identified. The cost of transcatheter closure as risk ascends is depicted (solid line). In D, the cost of operative closure as risk of readmission increases is depicted (dash-dot line) rather than the cost of transcatheter closure. The risk at which the 2 procedures are cost equivalent is marked with red dotted line. In C and D, there is no risk of readmission that results in cost equivalence.