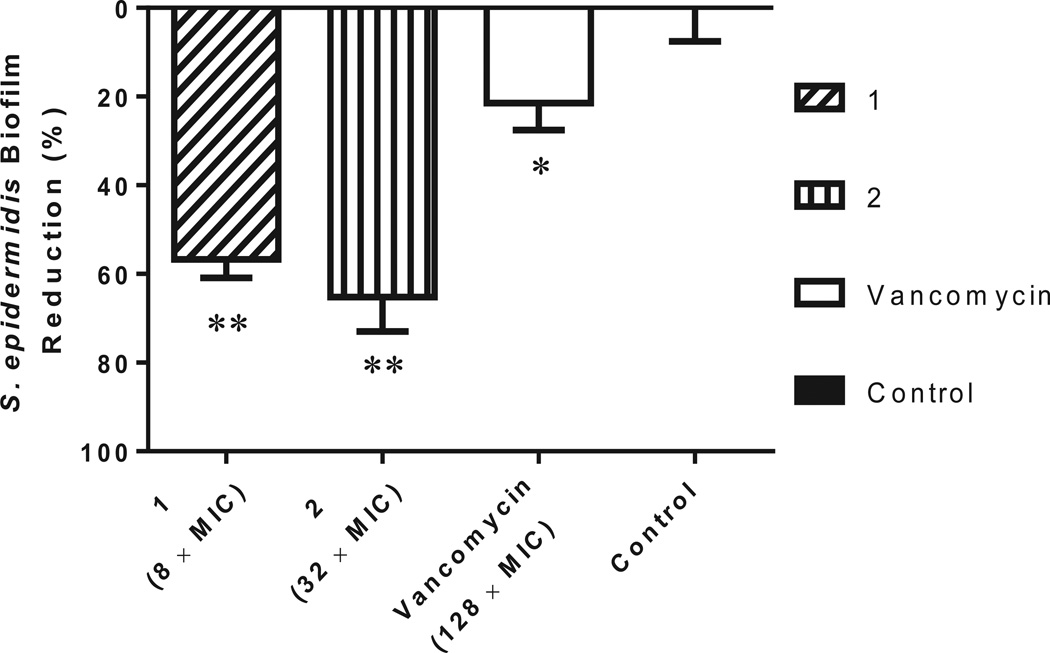
Figure 3.
Efficacy of thiazole compounds 1 and 2 and vancomycin (all at 64 µM) in disrupting an established methicillin-resistant S. epidermidis ATCC 35984 biofilm. Bacteria were incubated at 37°C in MHB medium supplemented with glucose for 24 h to allow biofilm formation. Wells were subsequently rinsed with PBS before MHB containing different concentrations of each test agent was added. Following incubation for 24 h, wells were washed again and left to dry. The adherent biofilm was stained with crystal violet and then the dye was extracted with ethanol before turbidity was measured at 595 nm. Data are presented as percentage of biofilm mass reduction compared to untreated wells (control). All experiments were done in triplicate. One asterisk (*) indicates data are statistically different when compared to the control (P < 0.05). Two asterisks (**) indicate the data are statistically different from the vancomycin-treated wells (P < 0.05).