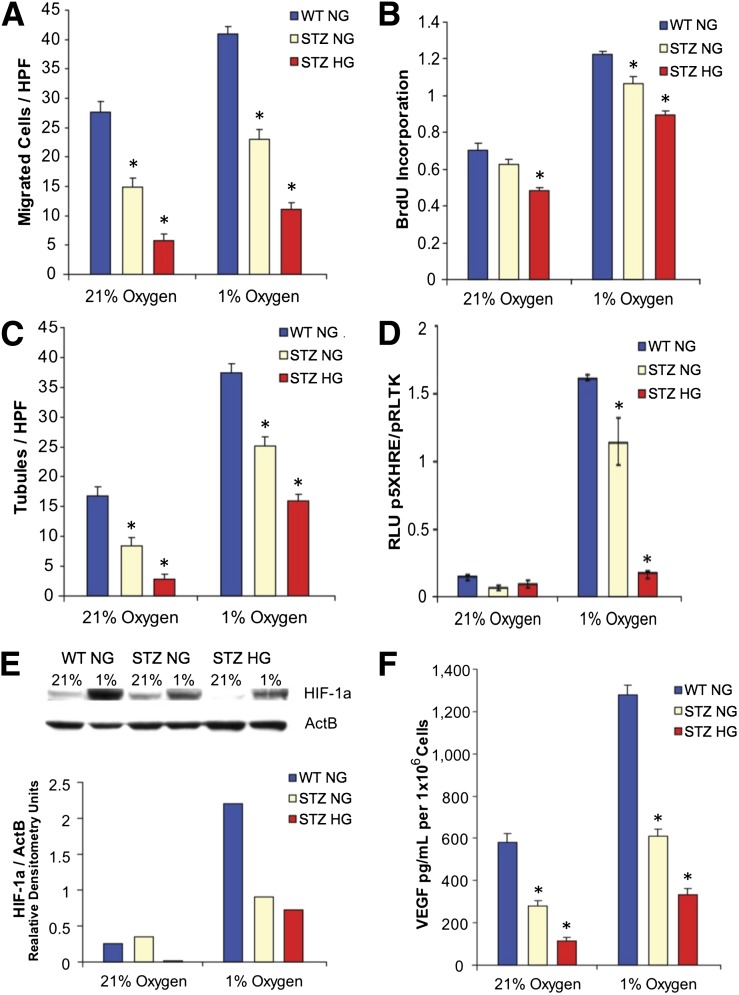
Figure 1.
Diabetic BM-MPCs have poor baseline vasculogenic properties in hyperoxia and hypoxia, functions that cannot be corrected with return to normal glucose levels. MPCs isolated from the bone marrow of type 1 diabetic (modeled by STZ) and WT mice were cultured in either 21% oxygen (hyperoxia) or 1% oxygen (hypoxia) under either normoglycemic (NG) (1 g/L) or hyperglycemic (HG) (4.5 g/L) glucose conditions. Diabetic BM-MPCs under all culture conditions exhibited a diminished ability to migrate toward a CXCL12 stimulus, a peptide critical for progenitor cell chemotaxis in vasculogenesis (A); undergo proliferation based on genomic BrdU incorporation studies (B); and form tubules in Matrigel when cocultured with b.End3 cells (C). D: HIF-1α transcriptional activity in STZ diabetic BM-MPCs, as measured by a firefly luciferase reporter plasmid using the VEGF HRE. E: Immunoblot and densitometry for HIF-1α protein demonstrate that diabetic BM-MPCs fail to stabilize HIF-1α in hypoxia. F: Diabetic BM-MPCs produce less VEGF-A in hyperoxic and hypoxic conditions as measured by ELISA on conditioned medium. HPF, high power field; RLU, relative light units. *P < 0.05 vs. WT group, n = 3.