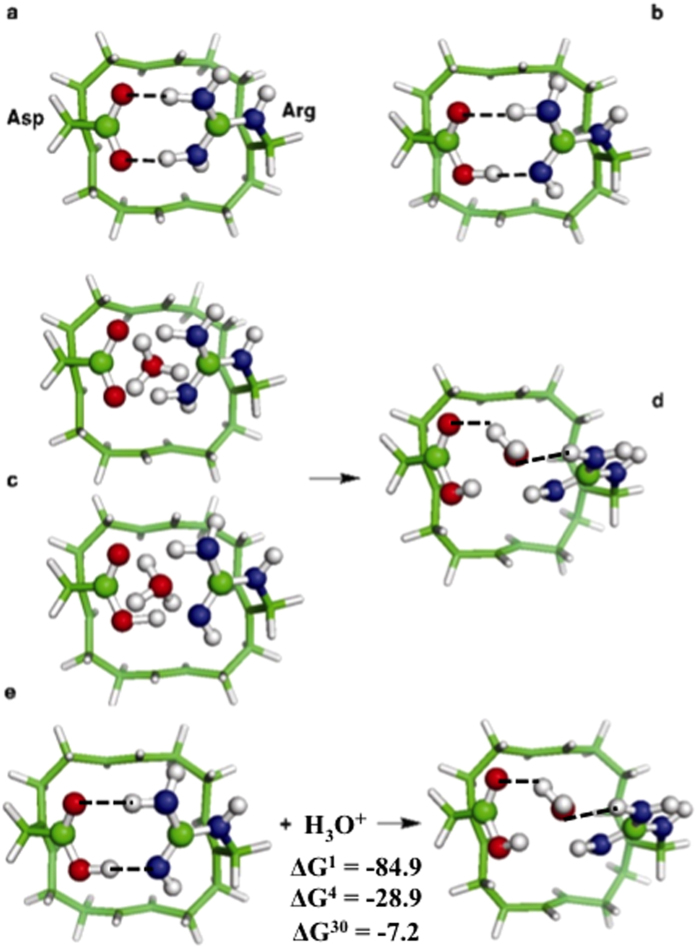
Figure 1. Binding of H3O+ to the Asp–Arg SF.
Fully optimized B3-LYP/6-31+G(3d,p) structures of (a) ion-free Asp––Arg+ SF, (b) Asp0–Arg0 SF, (c) initial configurations of the SF-H3O+ complex and (d) final configuration of the SF–H3O+ complex, AspH0–H2O–Arg+ with H in grey, C in green, N in blue and O in red. A dashed line denotes a hydrogen bond, which is defined by a donor–acceptor distance ≤3.5 Å and a H–acceptor distance ≤2.5 Å. The reaction between SF and H3O+ is depicted in (e) with free energies given in kcal/mol; ΔG1 is the binding free energy in the gas phase, whereas ΔG4 and ΔG30 are the corresponding free energies in the SF characterized by an effective dielectric constant of 4 and 30, respectively.